Blog
Articles about computational science and data science, neuroscience, and open source solutions. Personal stories are filed under Weekend Stories. Browse all topics here. All posts are CC BY-NC-SA licensed unless otherwise stated. Feel free to share, remix, and adapt the content as long as you give appropriate credit and distribute your contributions under the same license.
tags · RSS · Mastodon · simple view · page 1/19
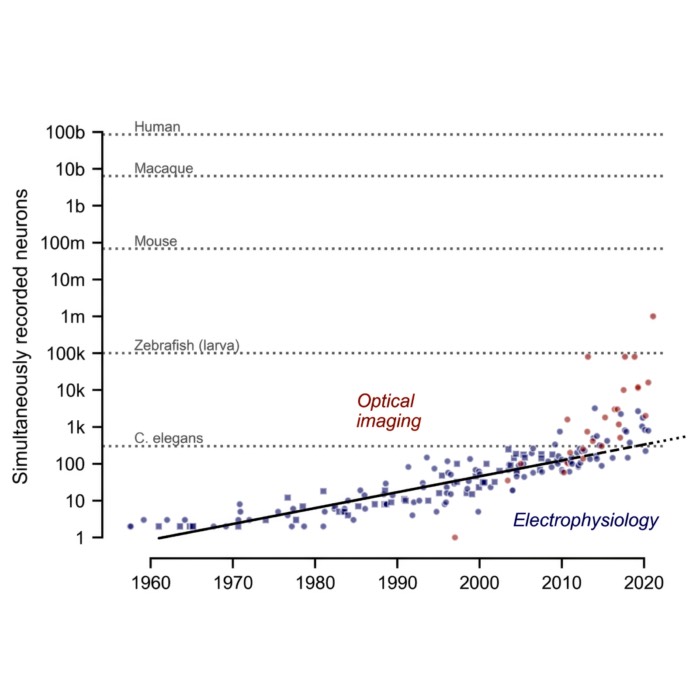
Revisiting the Moore’s law of Neuroscience, 15 years later
Just figured out that neuroscience appears to have its own version of Moore’s law, at least when it comes to the number of neurons that can be recorded simultaneously. This empirical scaling has profound implications for data analysis, modeling, and theory in computational neuroscience. In this post, we briefly review the original 2011 paper by Stevenson and Kording and reflect on its relevance today.
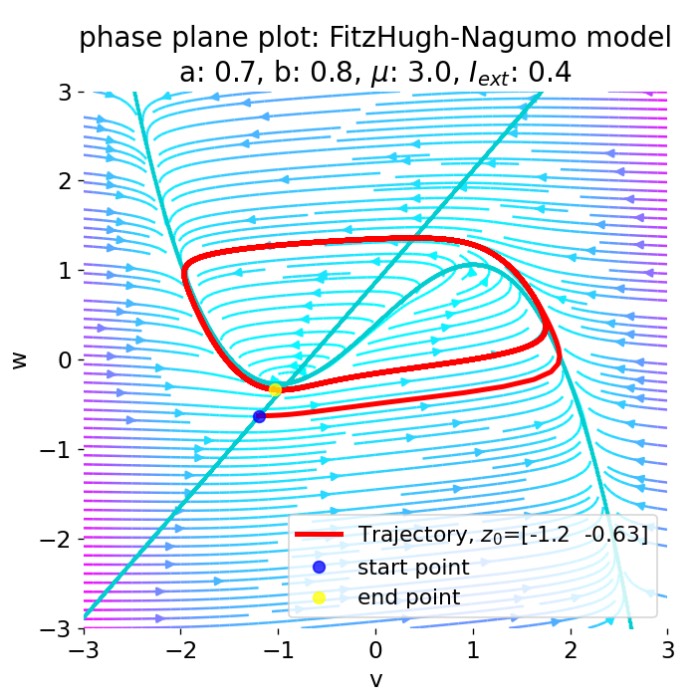
Neural Dynamics: A definitional perspective
Neural dynamics is a subfield of computational neuroscience that focuses on the time dependent evolution of neural activity and the mathematical structures that govern it. This post provides a definitional overview of neural dynamics, situating it within the broader context of computational neuroscience and outlining its key themes, methods, and historical developments.
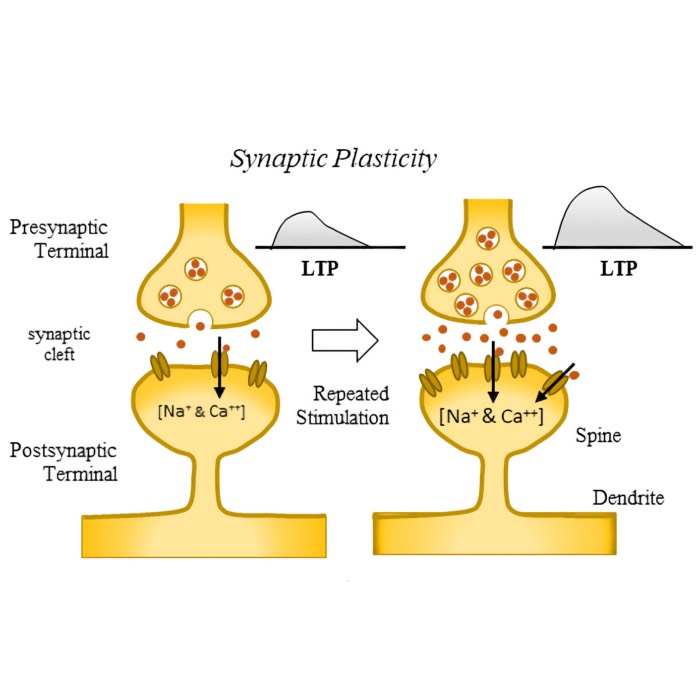
Neural plasticity and learning: A computational perspective
After discussing structural plasticity in the previous post, we now take a broader look at neural plasticity and learning from a computational perspective. What are the main forms of plasticity, how do they relate to learning, and how can we formalize these concepts in models of neural dynamics? In this post, we explore these questions and propose a unifying framework.
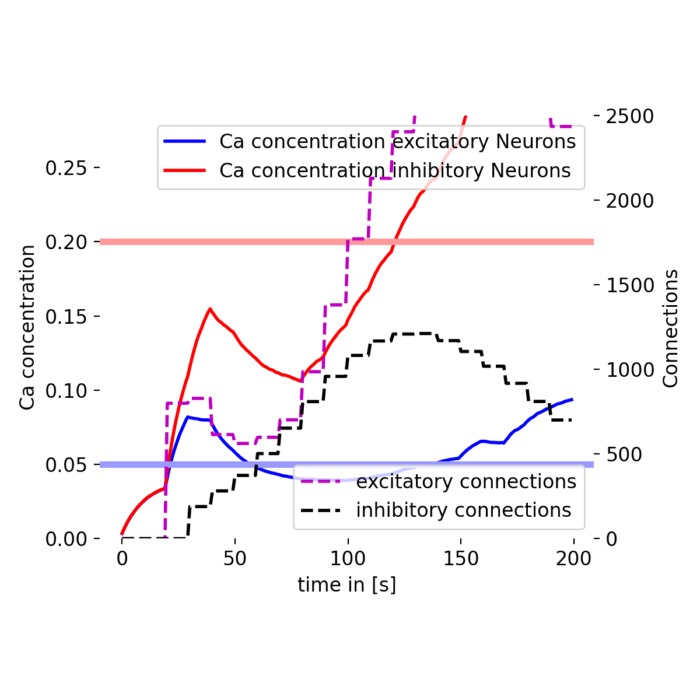
Incorporating structural plasticity in neural network models
In standard spiking neural networks (SNN), synaptic connections between neurons are typically fixed or change only according to specific plasticity rules, such as Hebbian learning or Spike-Timing Dependent Plasticity (STDP). However, the brain’s connectivity is not static. Neurons can grow and retract synapses in response to activity levels and environmental conditions. A phenomenon known as structural plasticity. This process plays a crucial role in learning and memory formation in the brain. To illustrate how structural plasticity can be modeled in spiking neural networks, in this post, we will use the NEST Simulator and replicate the tutorial on ‘Structural Plasticity.
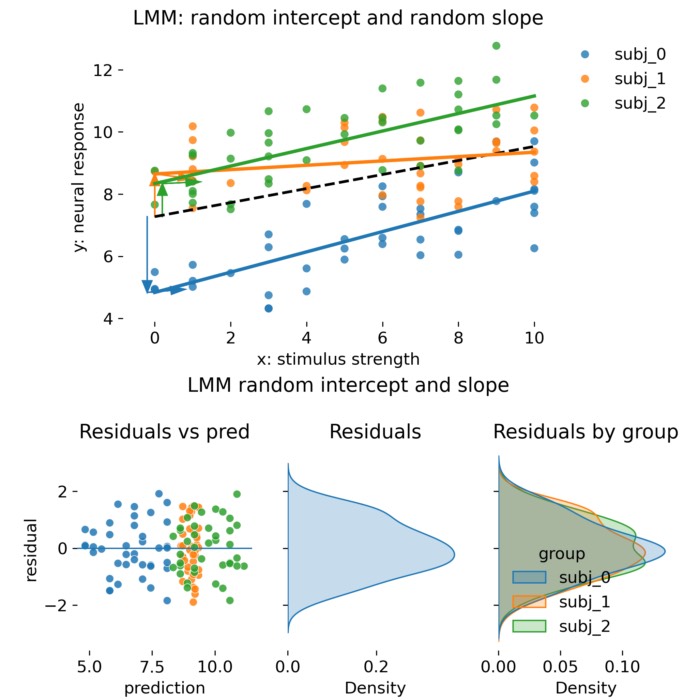
Linear mixed models in practice: When ANCOVA is enough and when you really need random effects
Linear mixed models (LMMs) are a powerful statistical tool for analyzing hierarchical or grouped data, common in neuroscience experiments. This post provides a practical guide on when to use LMMs versus traditional ANCOVA approaches, highlighting the advantages of mixed models in handling dependencies, unbalanced designs, and stabilizing estimates through shrinkage. Through simulated examples, we illustrate the differences in model performance and interpretation, helping you to make informed decisions about your statistical analyses.
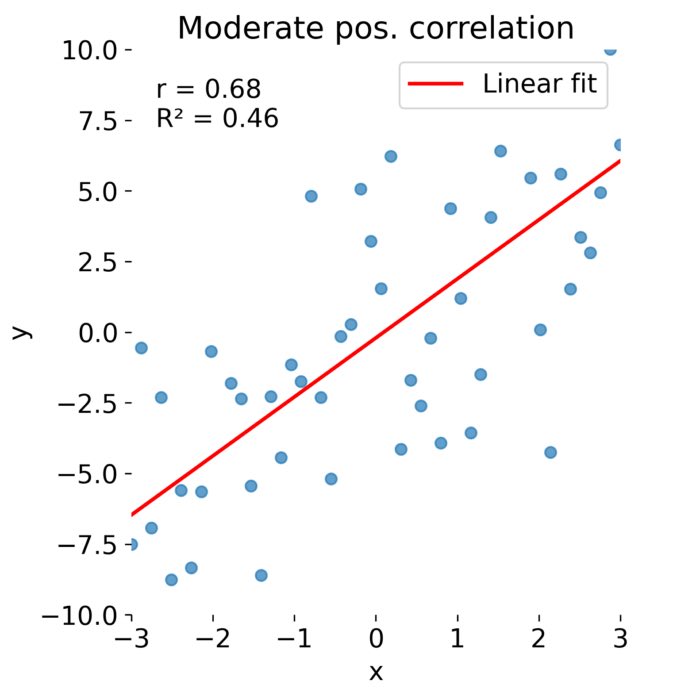
Distinguishing correlation from the coefficient of determination: Proper reporting of r and R²
I noticed that people sometimes report R² (‘R-squared’) instead of the Pearson correlation coefficient r when discussing the correlation between two variables. In the special case of a simple linear relationship this numerical equality is not strictly wrong, yet presenting R² as if it were the correlation coefficient might wrongly give the impression they are the same thing. In this post, we will therefore unpack the difference between these two measures, explain their mathematical definitions and proper usage discuss the best practices for when to use each in statistical reporting.
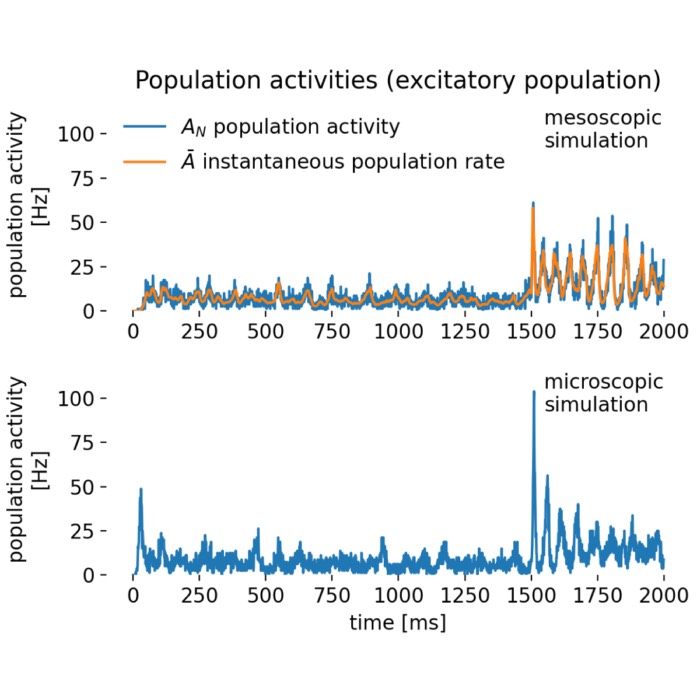
Rate models as a tool for studying collective neural activity
Rate models provide simplified representations of neural activity in which the precise spike timing of individual neurons is replaced by their average firing rate. This abstraction makes it possible to study the collective behavior of large neuronal populations and to analyze network dynamics in a tractable way. I recently played around with some rate models in Python, and in this post I’d like to share what I have learned so far about their implementation and utility.
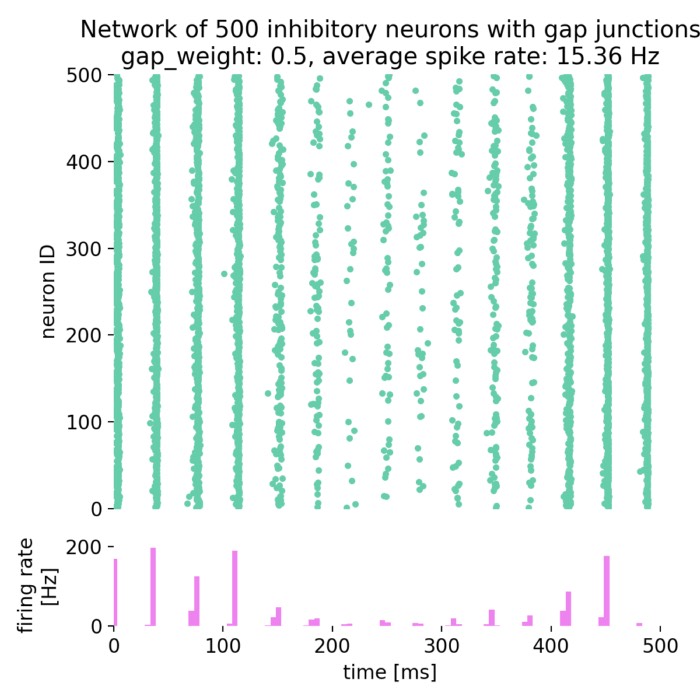
On the role of gap junctions in neural modelling: Network example
As a follow-up to our previous post on gap junctions, we will now explore how gap junctions can be implemented in a network of spiking neurons (SNN) using the NEST simulator. Gap junctions are electrical synapses that allow direct electrical communication between neurons, which can significantly influence the dynamics of neural networks.
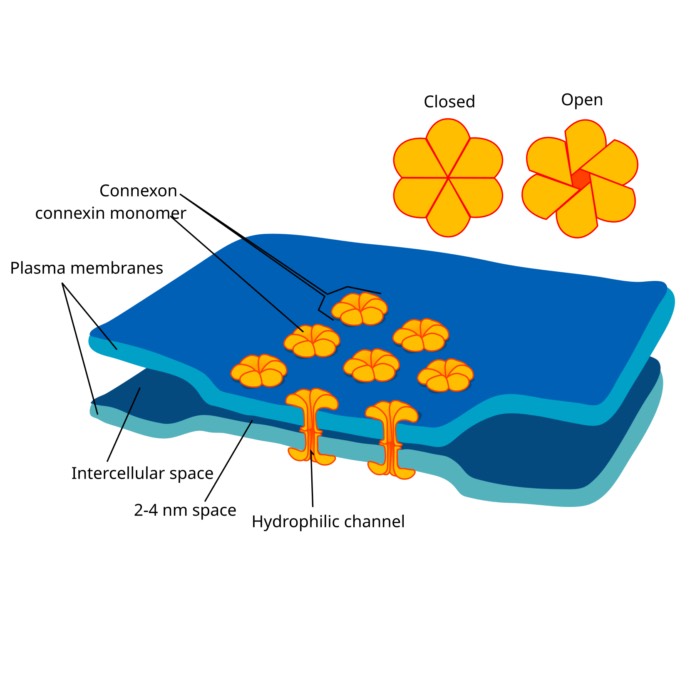
On the role of gap junctions in neural modelling
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections that facilitate direct electrical and chemical communication between neurons. Unlike synaptic transmission, which involves neurotransmitter release, gap junctions enable the direct passage of ions and small molecules through channels formed by connexins, leading to synchronized neuronal activity. In computational neuroscience, modeling gap junctions is crucial for understanding their role in neural network dynamics, synchronization, and various brain functions.
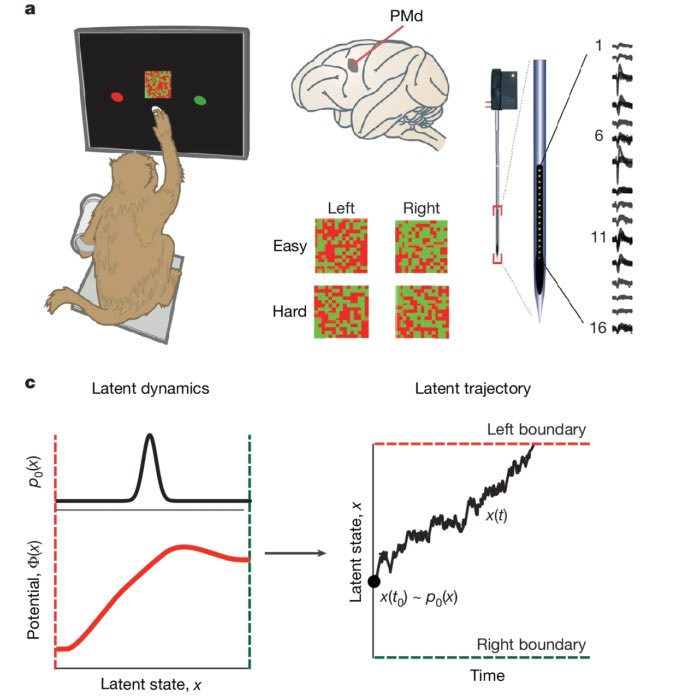
Shared dynamics, diverse responses: decoding decision-making in premotor cortex
Last week, I presented a recent study by Genkin et al., The dynamics and geometry of choice in the premotor cortex, in our Journal Club, and I found it conceptually compelling enough to summarize it here as well. The paper explores how perceptual decisions are encoded not in isolated neural responses but in population-wide latent dynamics. Traditionally, the neuroscience of decision-making has focused on ramping activity in individual neurons, heterogeneous peristimulus time histograms (PSTHs), and decoding strategies based on trial-averaged firing rates. In contrast, this work proposes that a shared low-dimensional decision variable evolves over time and explains the observed diversity in single-neuron responses. In our discussion, we focused on the paper’s central figures, using them to guide a step-by-step reconstruction of the study’s logic and findings.