#Computational Science
Computational Science is where most of my day to day scientific work eventually ends up. So, it’s not surprising that I also write about it on this blog. Posts tagged this way usually revolve around building executable models of physical and biological systems, running simulations, and turning data into something that can actually be reasoned about. These days this mostly means computational neuroscience, while earlier work focused more strongly on plasma and space physics. For all these fields, my emphasis usually lies on numerical experiments, statistical analysis, and reproducible research pipelines.
There are currently 84 articles with this tag (newest first):
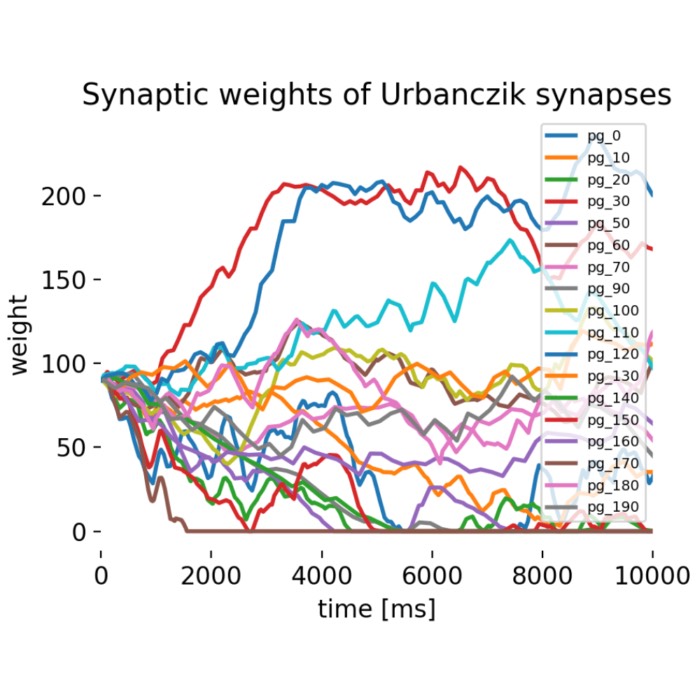
Urbanczik-Senn plasticity
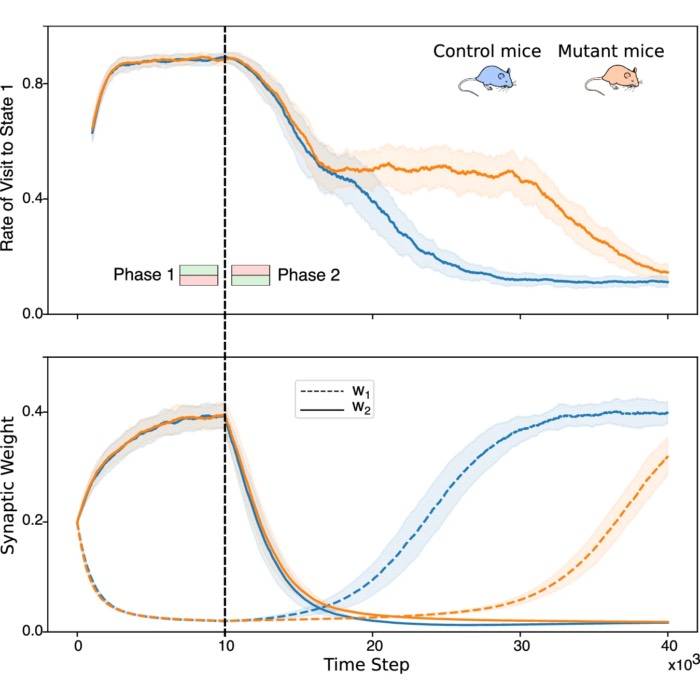
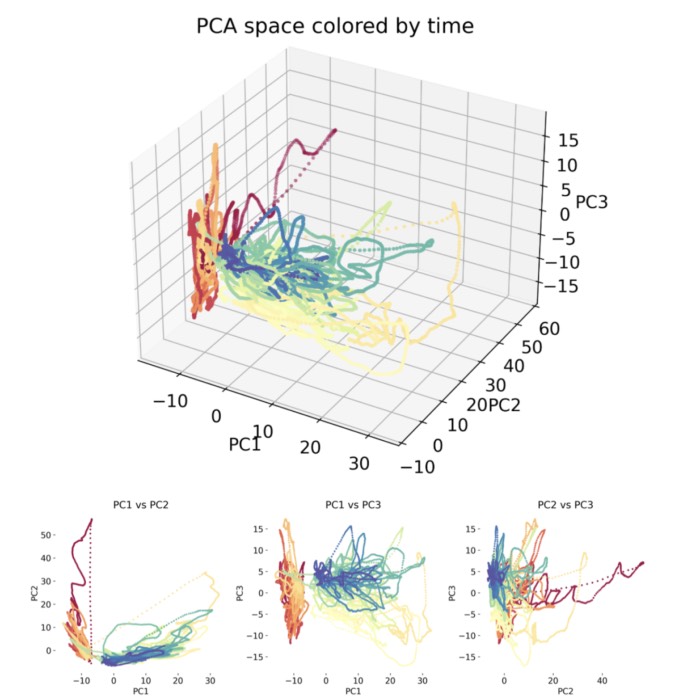
The Urbanczik-Senn plasticity model proposes a learning rule for dendritic synapses in a simplifi...
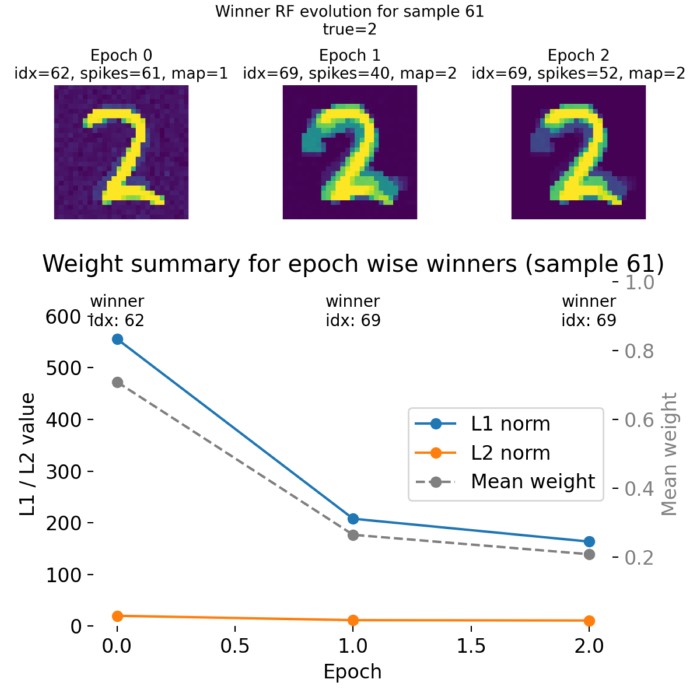
Implementing a minimal spiking neural network for MNIST pattern recognition using nervos
In this post, we use the open source spiking neural network (SNN) framework nervos to implement a...
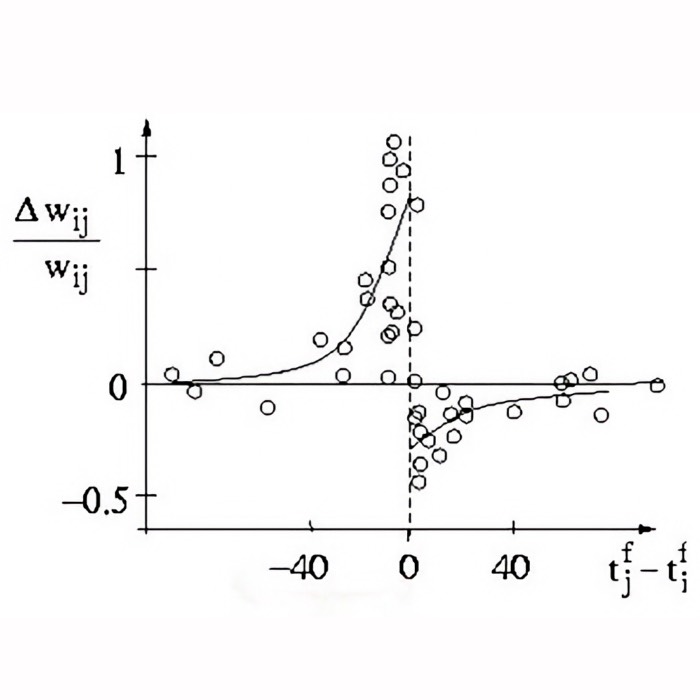
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP)
Another frequently used term in computational neuroscience is spike-timing-dependent plasticity o...
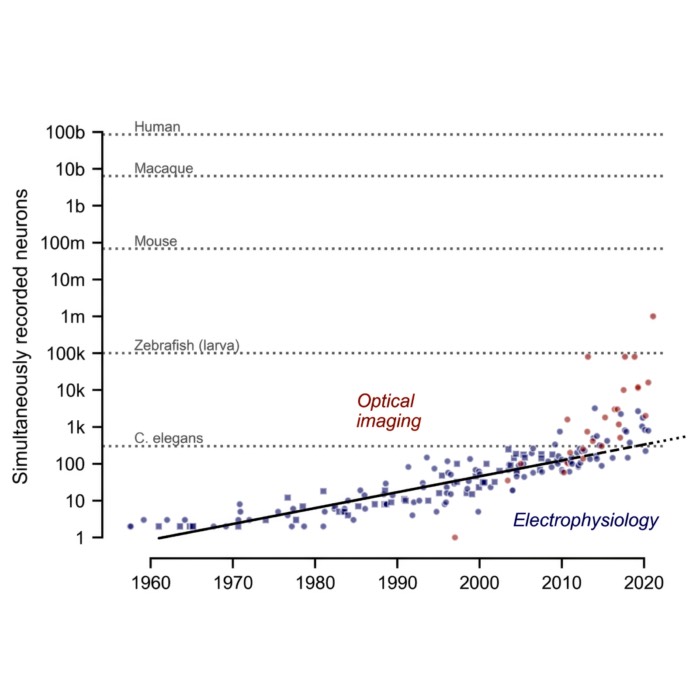
Revisiting the Moore’s law of Neuroscience, 15 years later
Just figured out that neuroscience appears to have its own version of Moore’s law, at least when ...
Neural Dynamics: A definitional perspective
Neural dynamics is a subfield of computational neuroscience that focuses on the time dependent ev...
Neural plasticity and learning: A computational perspective
After discussing structural plasticity in the previous post, we now take a broader look at neural...
Incorporating structural plasticity in neural network models
In standard spiking neural networks (SNN), synaptic connections between neurons are typically fix...
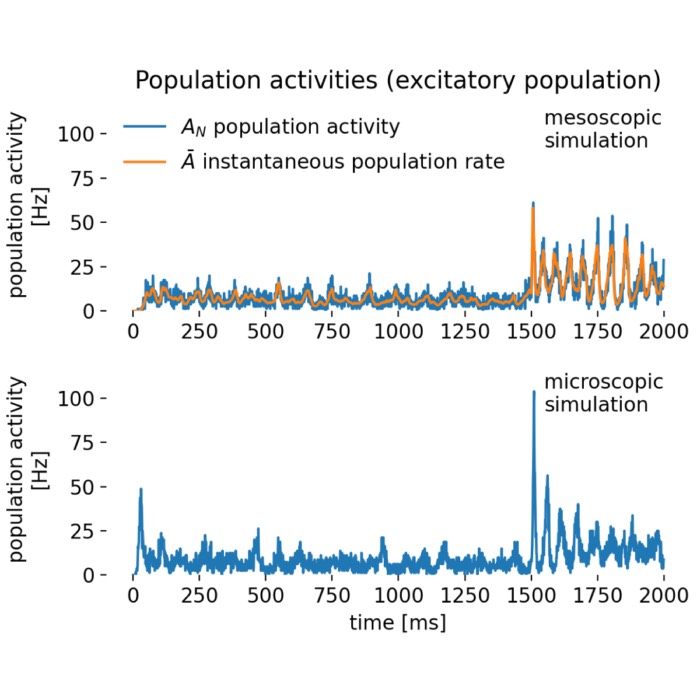
Rate models as a tool for studying collective neural activity
Rate models provide simplified representations of neural activity in which the precise spike timi...
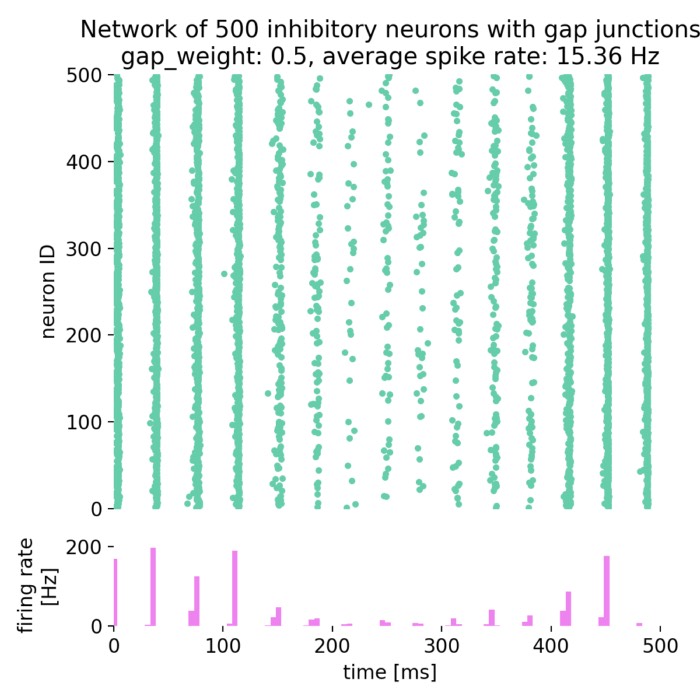
On the role of gap junctions in neural modelling: Network example
As a follow-up to our previous post on gap junctions, we will now explore how gap junctions can b...
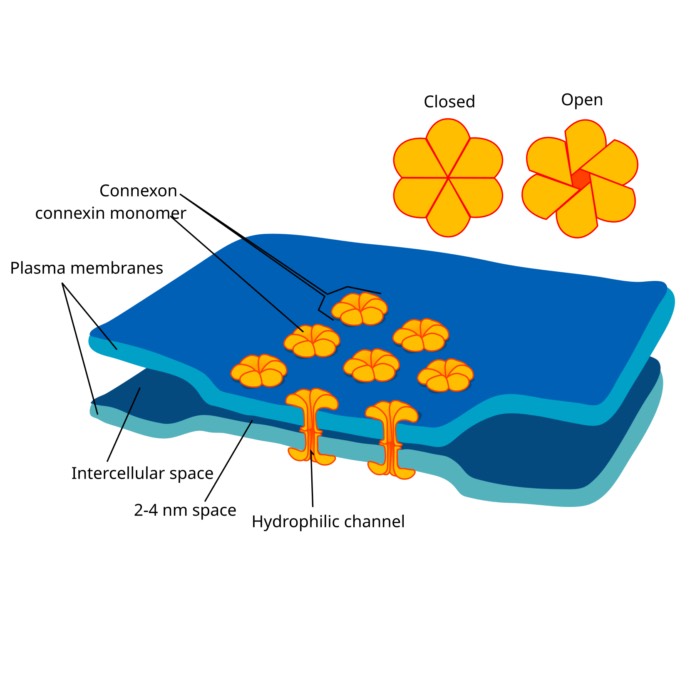
On the role of gap junctions in neural modelling
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections that facilitate direct electrical and che...
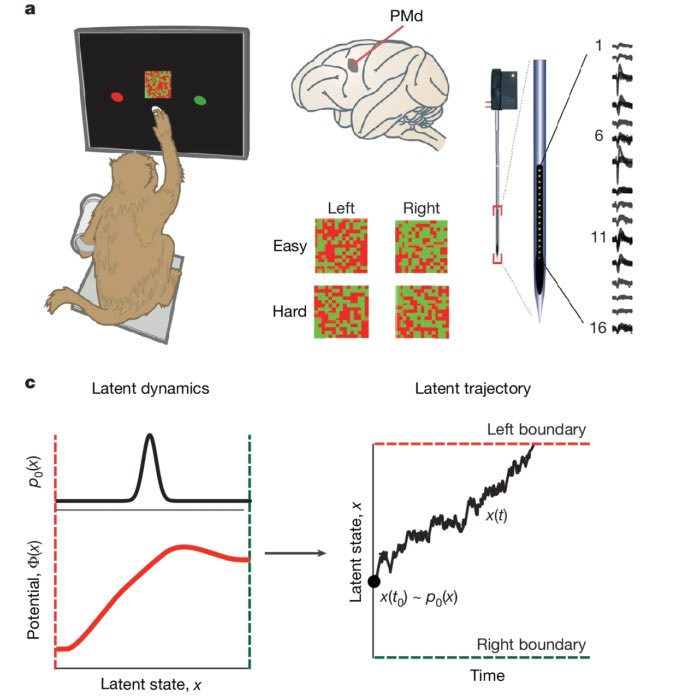
Shared dynamics, diverse responses: decoding decision-making in premotor cortex
Last week, I presented a recent study by Genkin et al., The dynamics and geometry of choice in th...
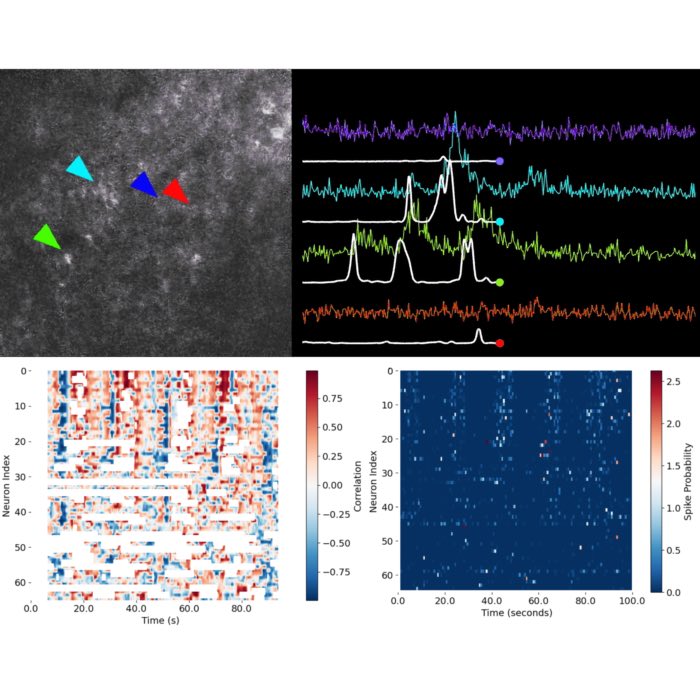
New teaching material: Functional imaging data analysis – From calcium imaging to network dynamics
We have just completed our new course, Functional Imaging Data Analysis: From Calcium Imaging to ...
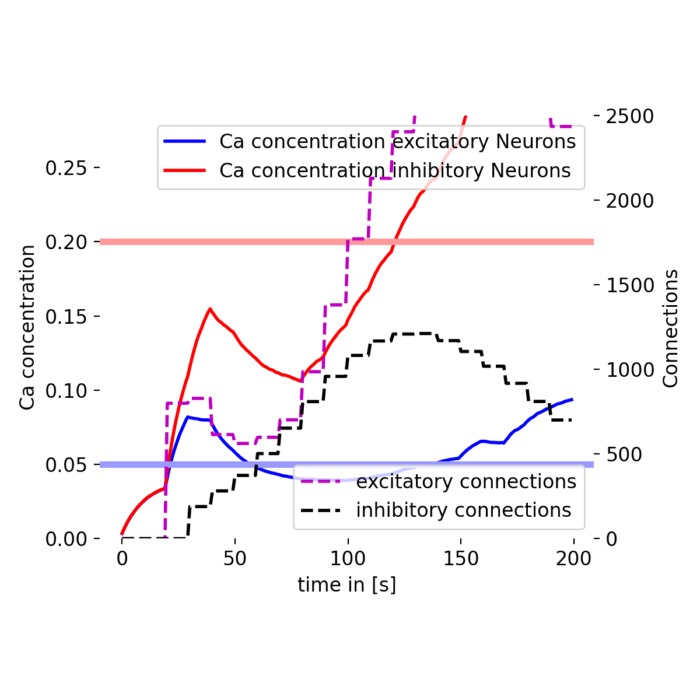
Astrocytes enhance plasticity response during reversal learning
Astrocytes, a type of glial cell traditionally considered support cells in the brain, are now rec...
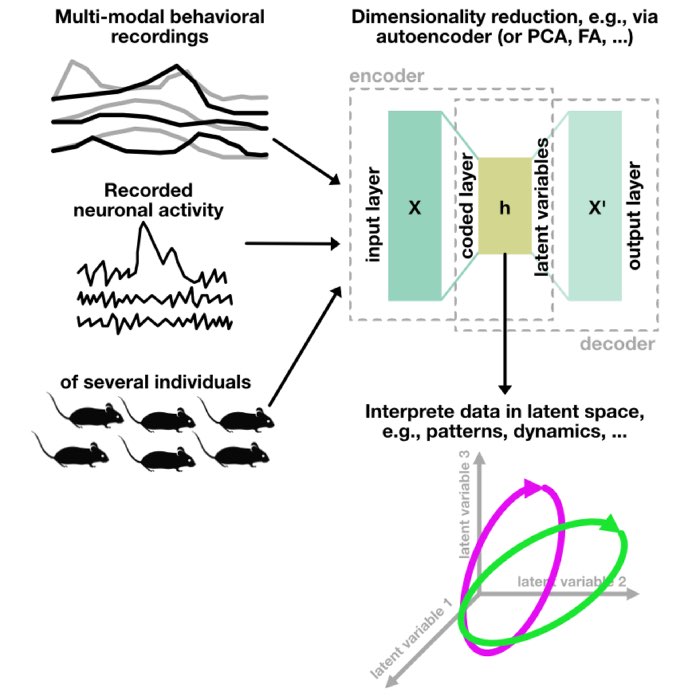
New teaching material: Dimensionality reduction in neuroscience
We just completed a new two-day course on Dimensionality Reduction in Neuroscience, and I am plea...
Long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD)
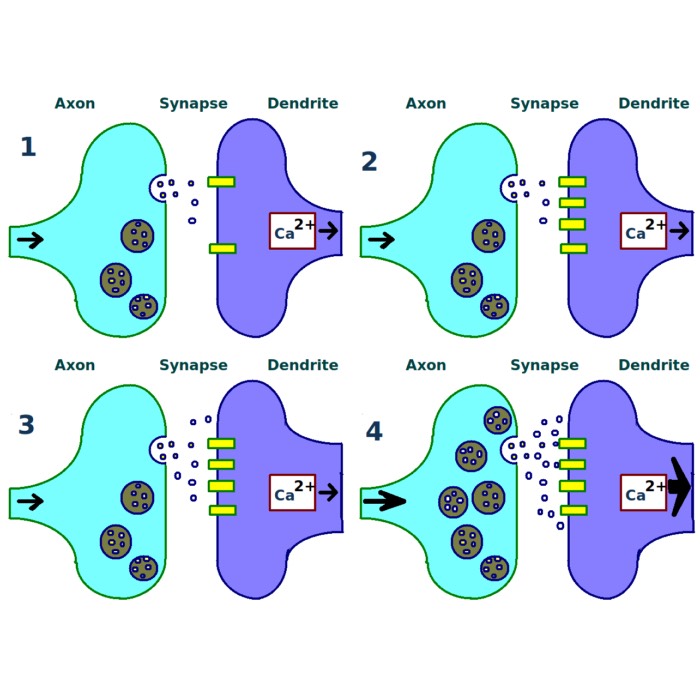
Both long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) are forms of synaptic plasticity...
Bienenstock-Cooper-Munro (BCM) rule
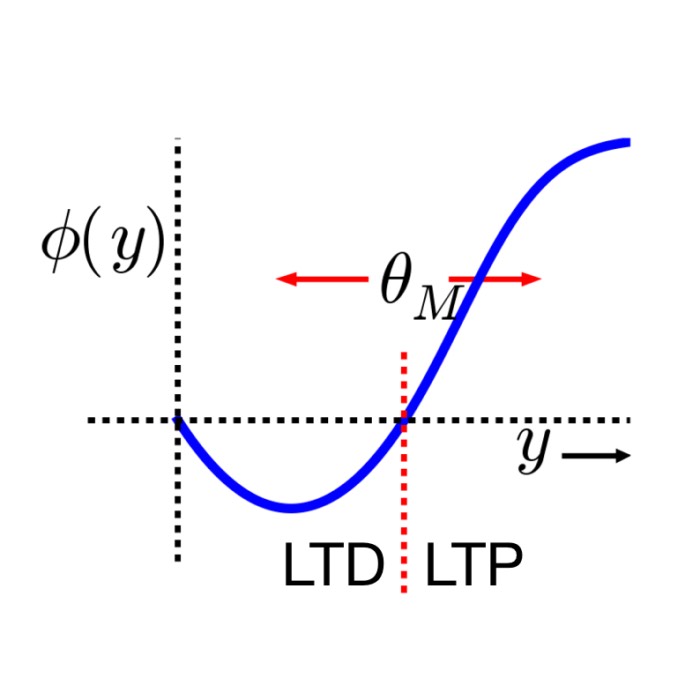
The Bienenstock-Cooper-Munro (BCM) rule is a cornerstone in theoretical neuroscience, offering a ...
Campbell and Siegert approximation for estimating the firing rate of a neuron
The Campbell and Siegert approximation is a method used in computational neuroscience to estimate...
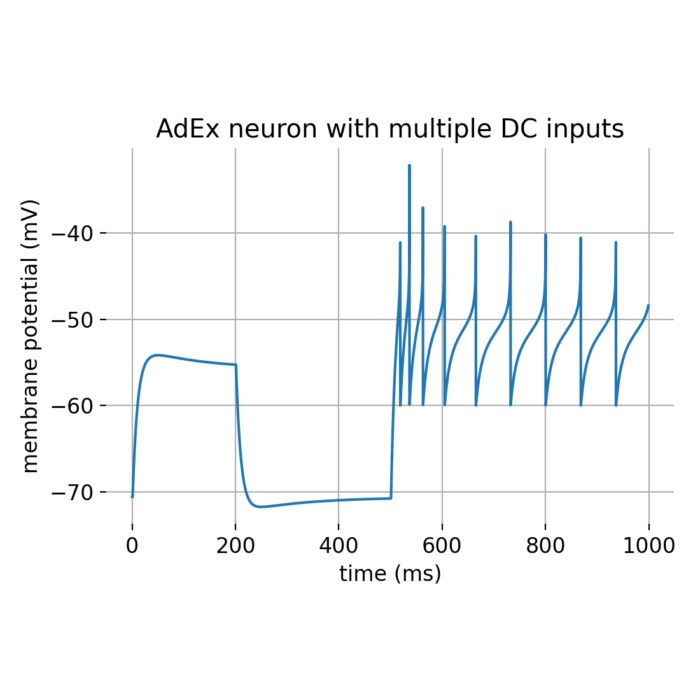
Exponential (EIF) and adaptive exponential Integrate-and-Fire (AdEx) model
The exponential Integrate-and-Fire (EIF) model is a simplified neuronal model that captures the e...
Olfactory processing via spike-time based computation
In their work ‘Simple Networks for Spike-Timing-Based Computation, with Application to Olfactory ...
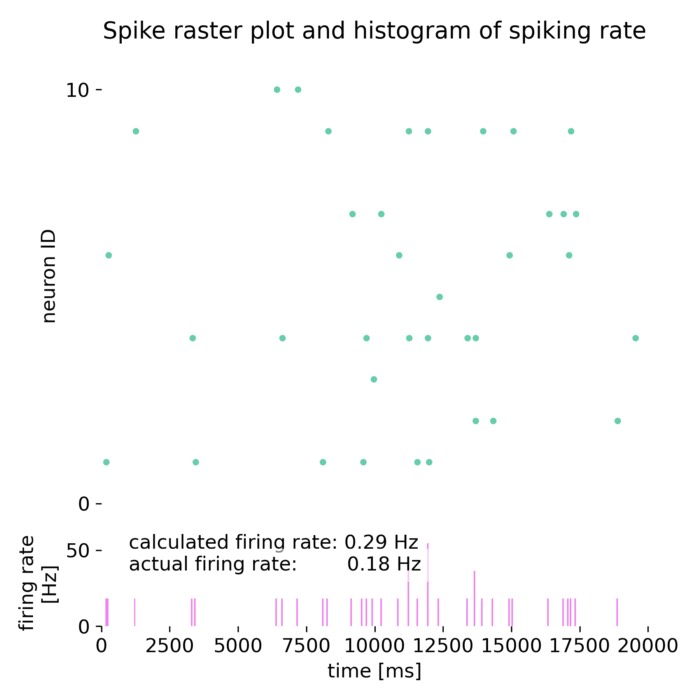
Frequency-current (f-I) curves
In this short tutorial, we will explore the concept of frequency-current (f-I) curves exemplified...
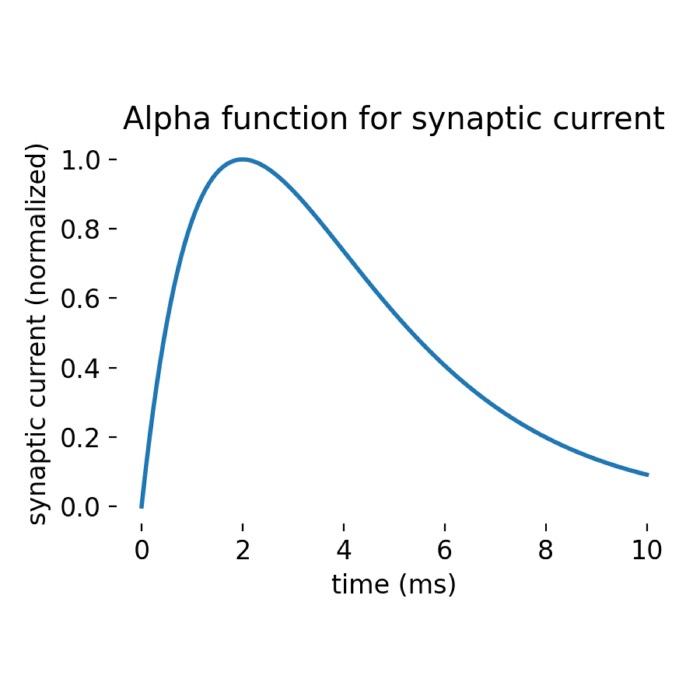
What are alpha-shaped post-synaptic currents?
In some recent posts, we have applied a specific type of integrate-and-fire neuron model, the iaf...
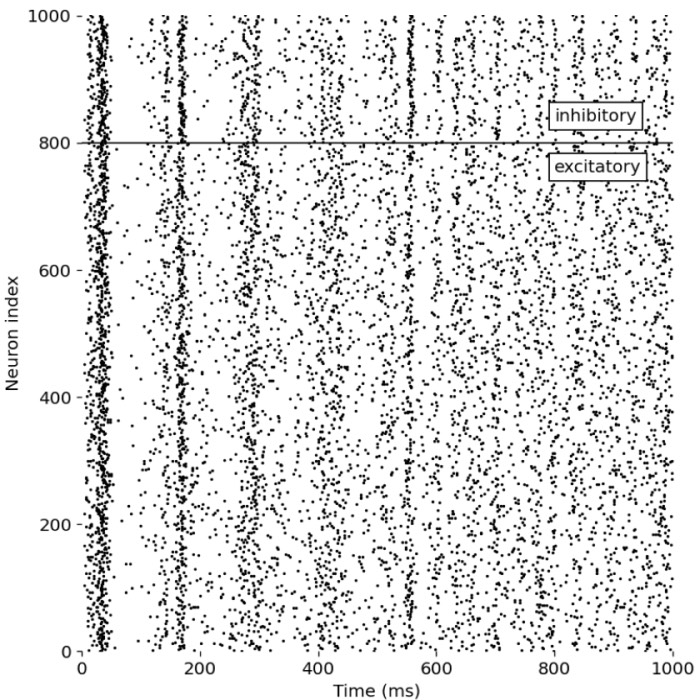
Example of a neuron driven by an inhibitory and excitatory neuron population
In this tutorial, we recap the NEST tutorial ‘Balanced neuron example’. We will simulate a neuron...
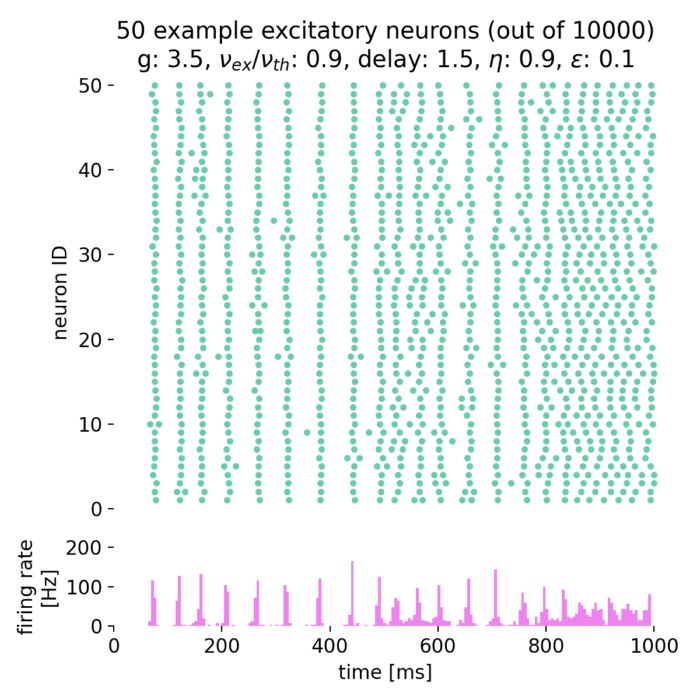
Brunel network: A comprehensive framework for studying neural network dynamics
In his work from 2000, Nicolas Brunel introduced a comprehensive framework for studying the dynam...
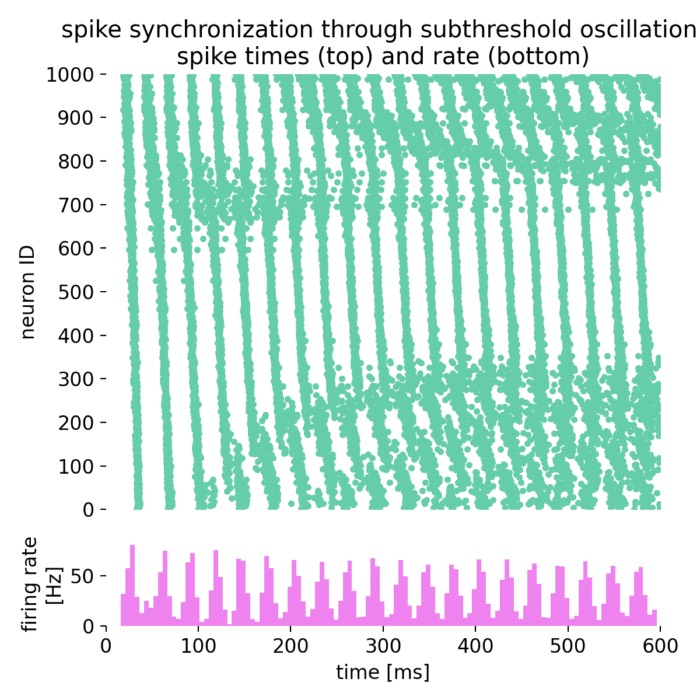
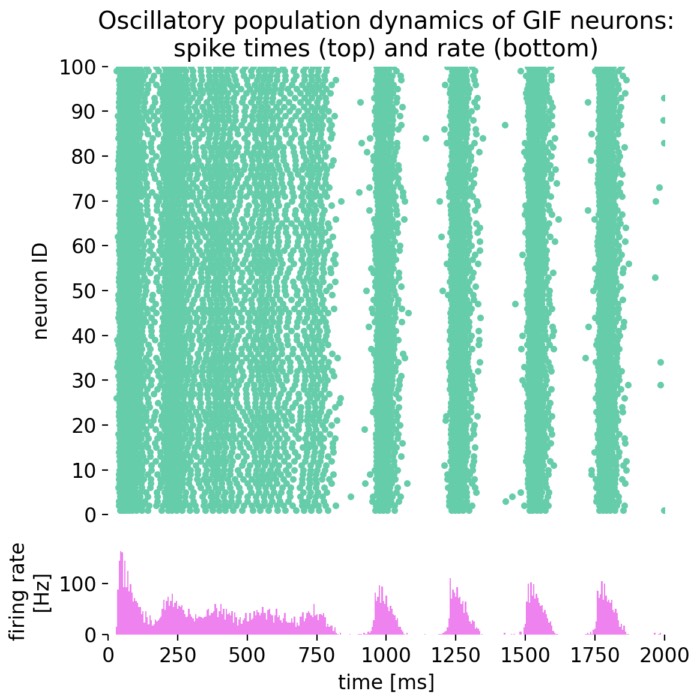
Oscillatory population dynamics of GIF neurons simulated with NEST
In this tutorial, we will explore the oscillatory population dynamics of generalized integrate-an...
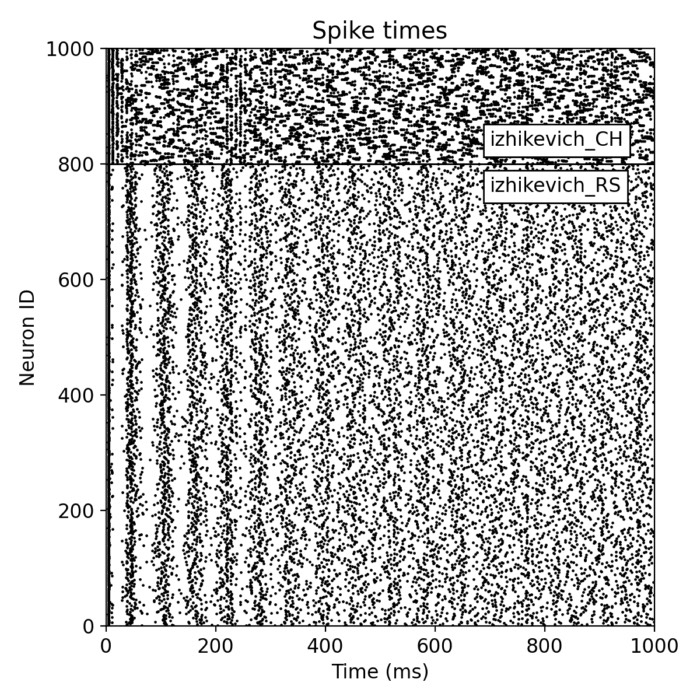
Izhikevich SNN simulated with NEST
In this post, we explore how easy it is to set up a large-scale, multi-population spiking neural...
Connection concepts in NEST
In the previous post, we learned about the basic concepts of the NEST simulator and how to create...
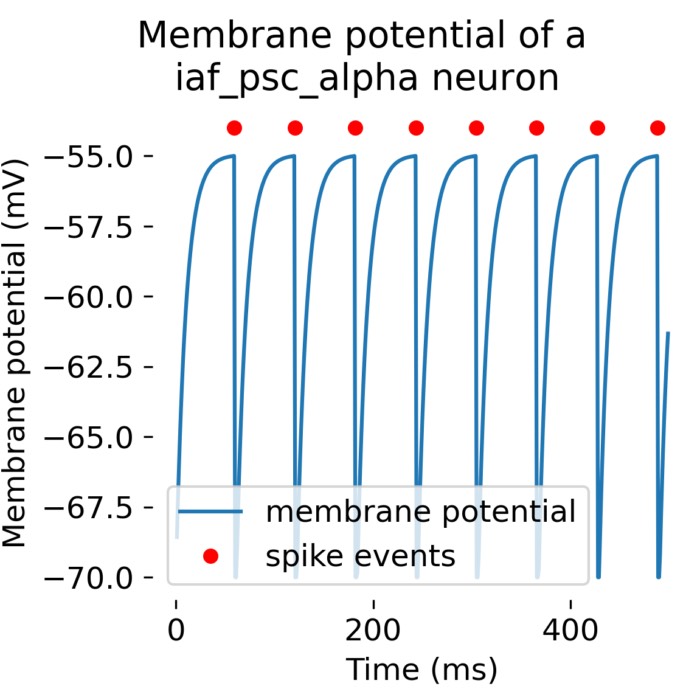
Step-by-step NEST single neuron simulation
While NEST is designed for large-scale simulations of neural spike networks, the underlying model...
NEST simulator – A powerful tool for simulating large-scale spiking neural networks
The NEST simulator is a powerful software tool designed for simulating large-scale networks of sp...
Simulating spiking neural networks with Izhikevich neurons
The Izhikevich neuron model that we have discussed earlier is known for its simplicity and comput...
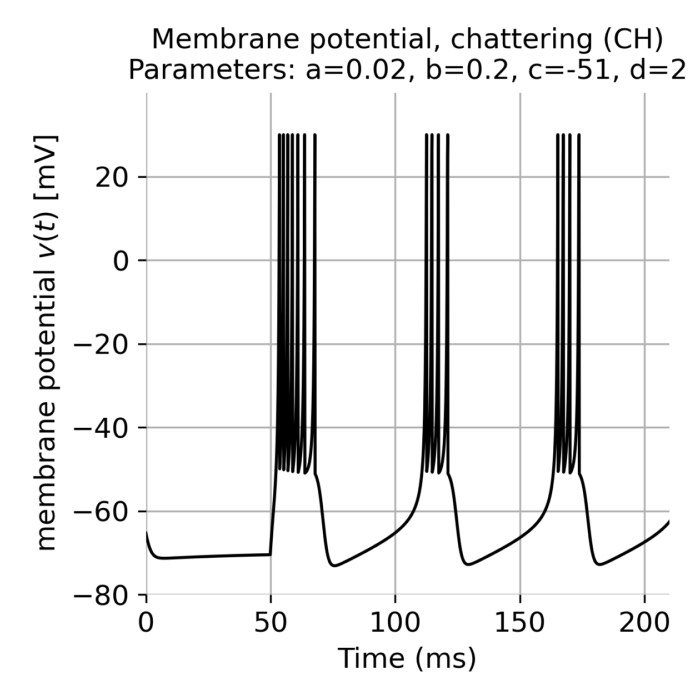
Izhikevich model
Computational neuroscience utilizes mathematical models to understand the complex dynamics of neu...
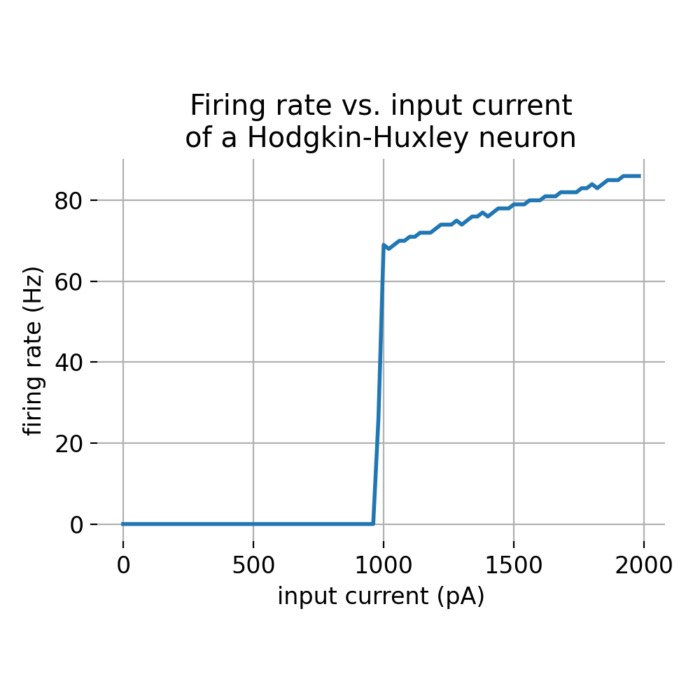
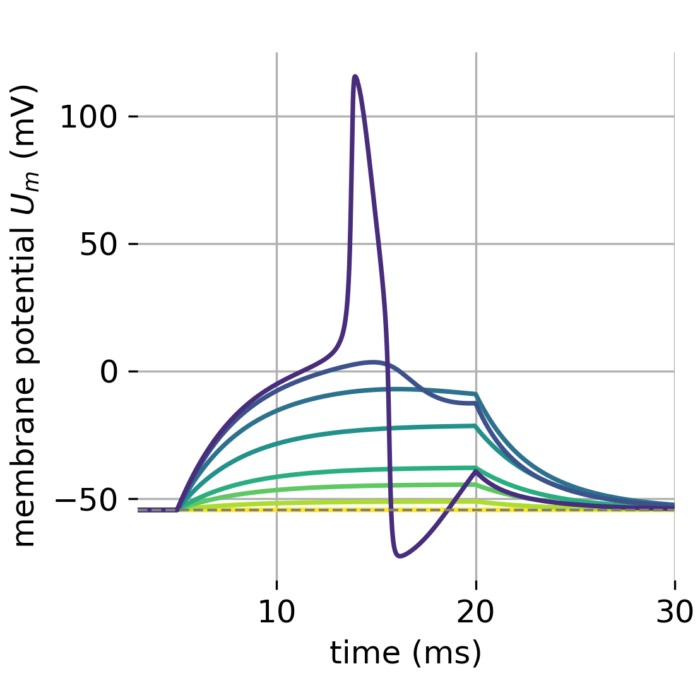
Hodgkin-Huxley model
An important step beyond simplified neuronal models is the Hodgkin-Huxley model. This model is ba...
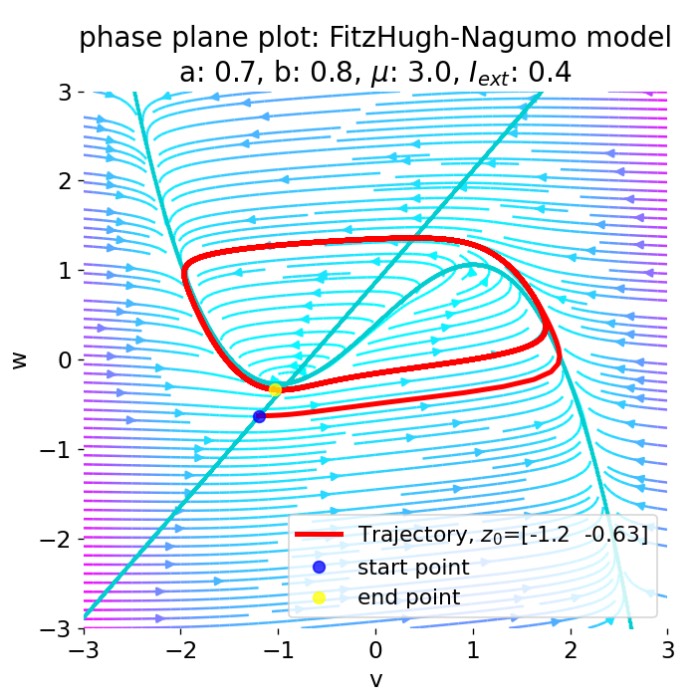
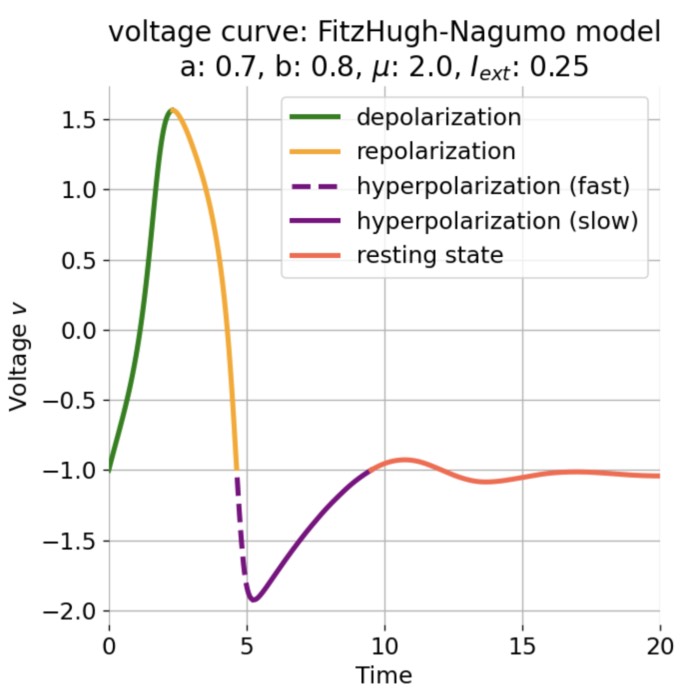
FitzHugh-Nagumo model
In the previous post, we analyzed the dynamics of Van der Pol oscillator by using phase plane an...
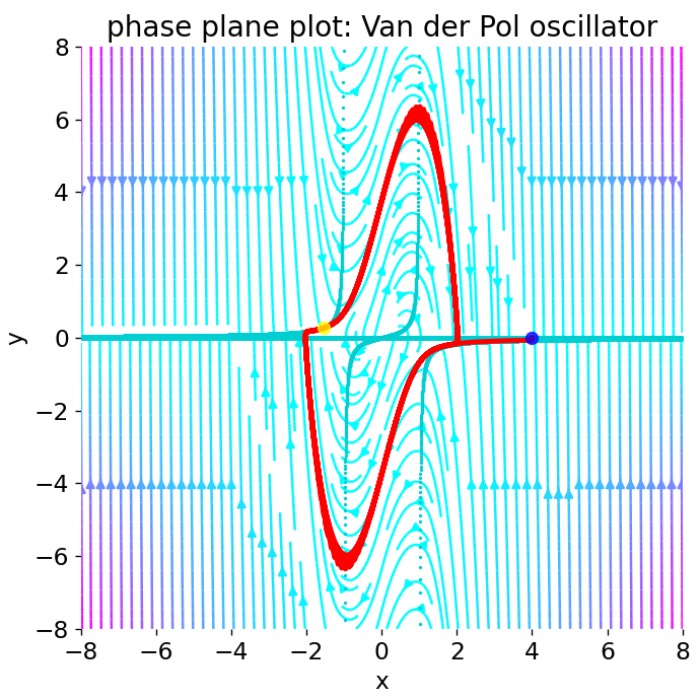
Van der Pol oscillator
In this post, we will apply phase plane analysis to the Van der Pol oscillator. The Van der Pol o...
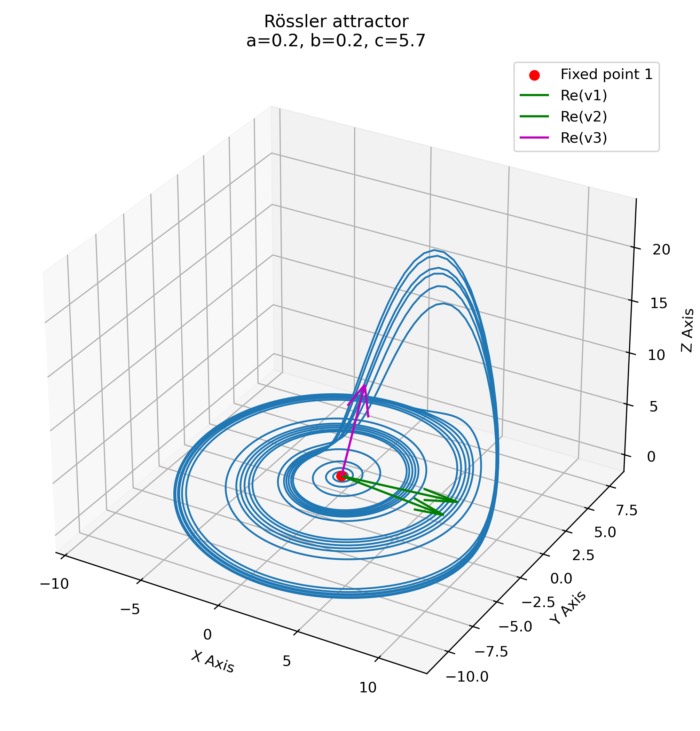
Nullclines and fixed points of the Rössler attractor
After introducing phase plane analysis in the previous post, we will now apply this method to the...
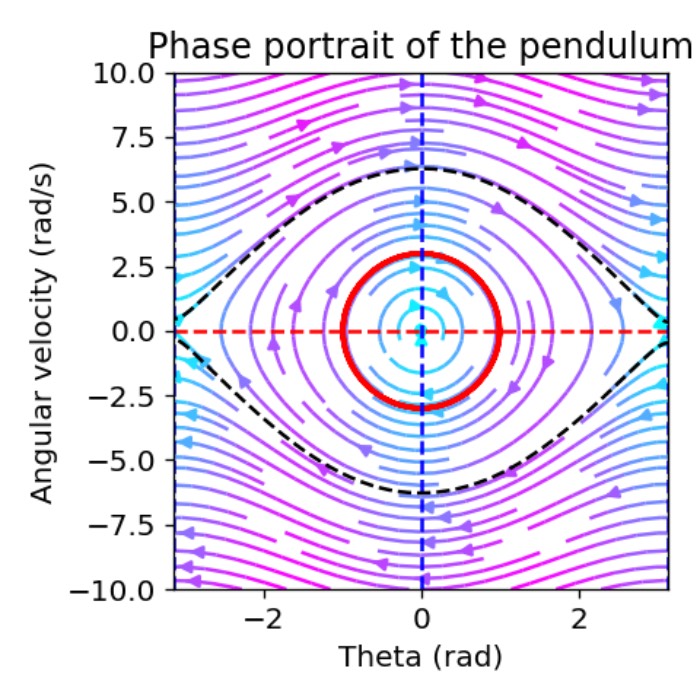
Using phase plane analysis to understand dynamical systems
When it comes to understanding the behavior of dynamical systems, it can quickly become too comp...
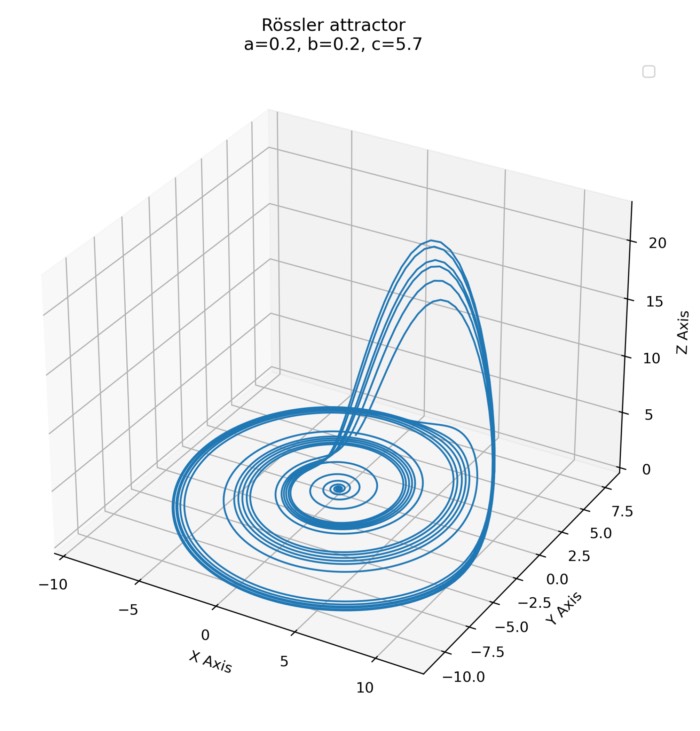
Rössler attractor
Unlike the Lorenz attractor which emerges from the dynamics of convection rolls, the Rössler attr...
Understanding Hebbian learning in Hopfield networks
Hopfield networks, a form of recurrent neural network (RNN), serve as a fundamental model for und...
Building a neural network from scratch using NumPy
Ever thought about building you own neural network from scratch by simply using NumPy? In this po...
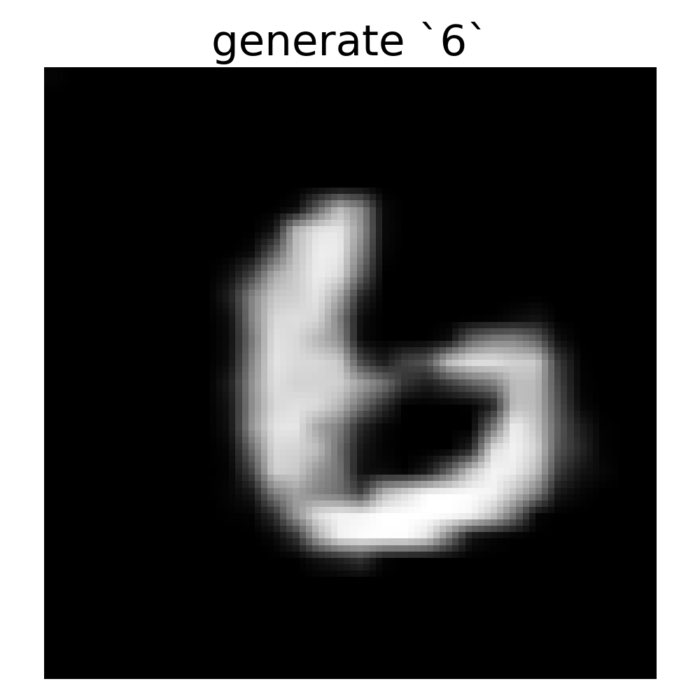
Conditional GANs
I was wondering whether it would be possible to let GANs generate samples conditioned on a specif...
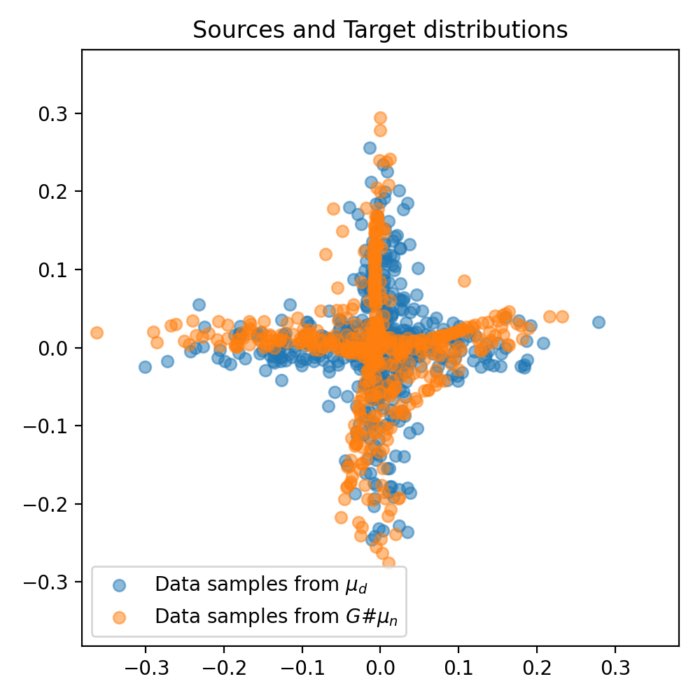
Eliminating the middleman: Direct Wasserstein distance computation in WGANs without discriminator
We explore an alternative approach to implementing WGANs. Contrasting from the standard implemen...
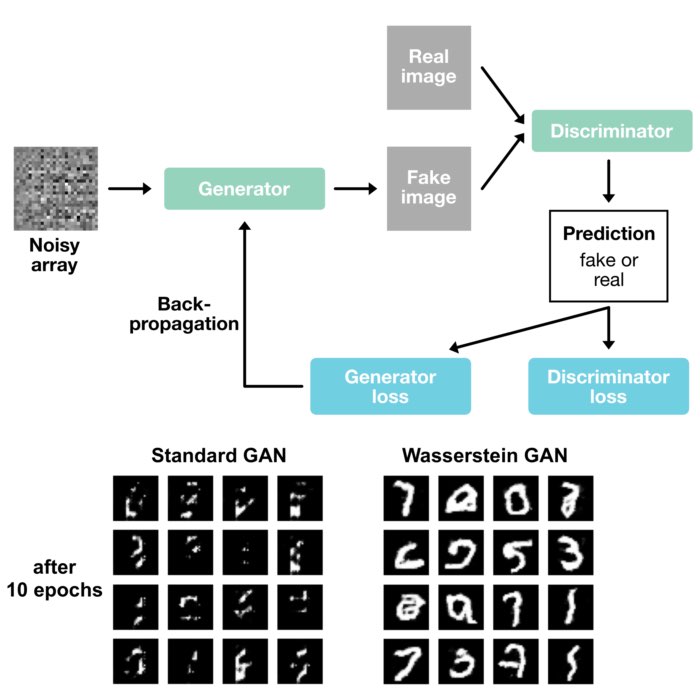
Wasserstein GANs
We apply the Wasserstein distance to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to train them more ef...
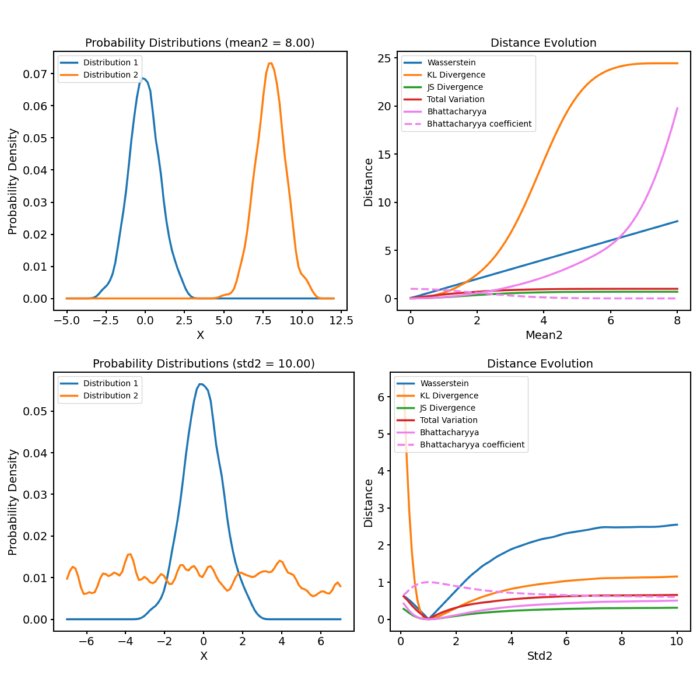
Probability distance metrics in machine learning
Probabilistic distance metrics play a crucial role in a broad range of machine learning tasks, in...
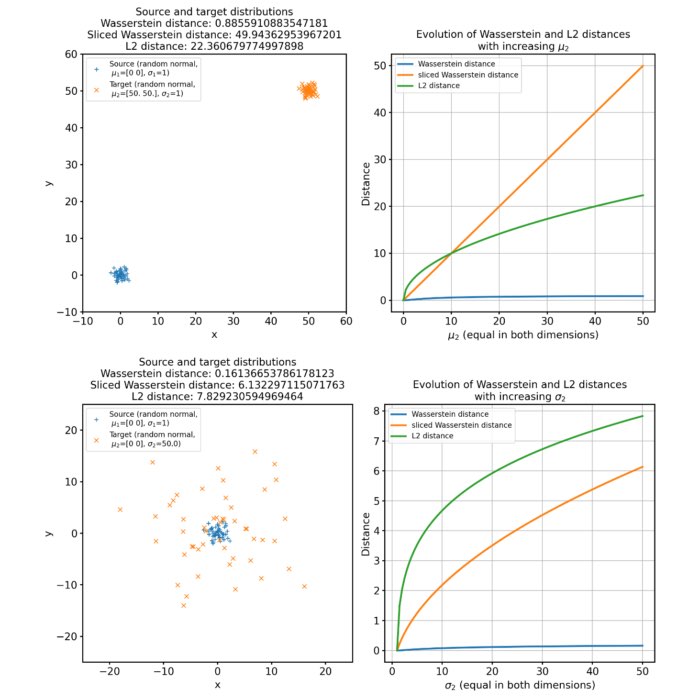
Comparing Wasserstein distance, sliced Wasserstein distance, and L2 norm
In machine learning, especially when dealing with probability distributions or deep generative mo...
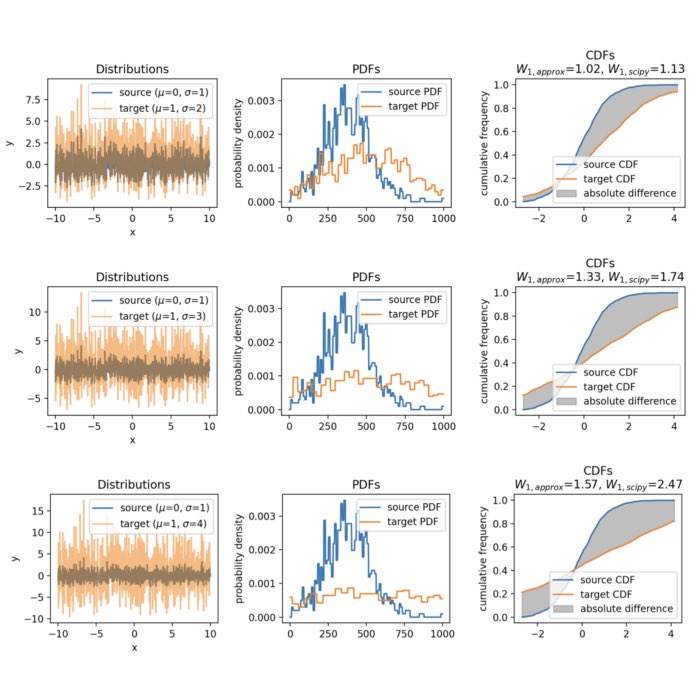
Approximating the Wasserstein distance with cumulative distribution functions
In the previous two posts, we’ve discussed the mathematical details of the Wasserstein distance, ...
Wasserstein distance via entropy regularization (Sinkhorn algorithm)
Calculating the Wasserstein distance can be computational costly when using linear programming. T...
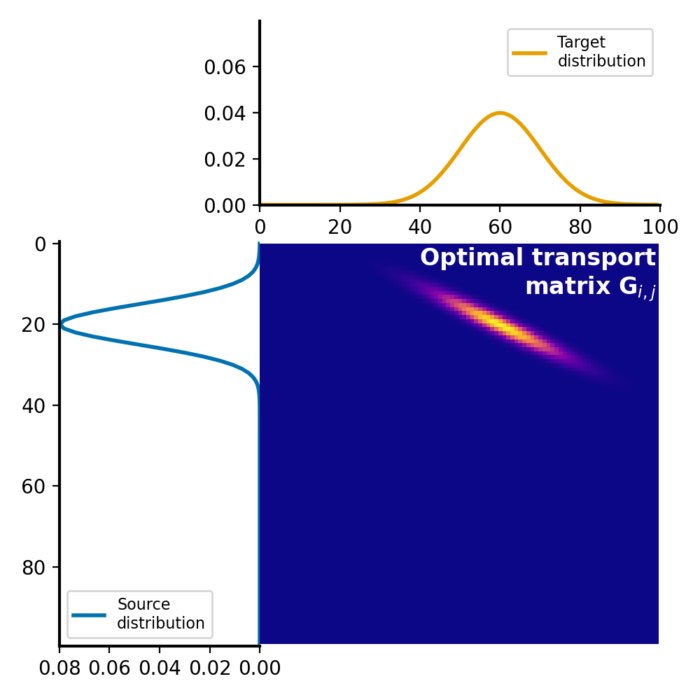
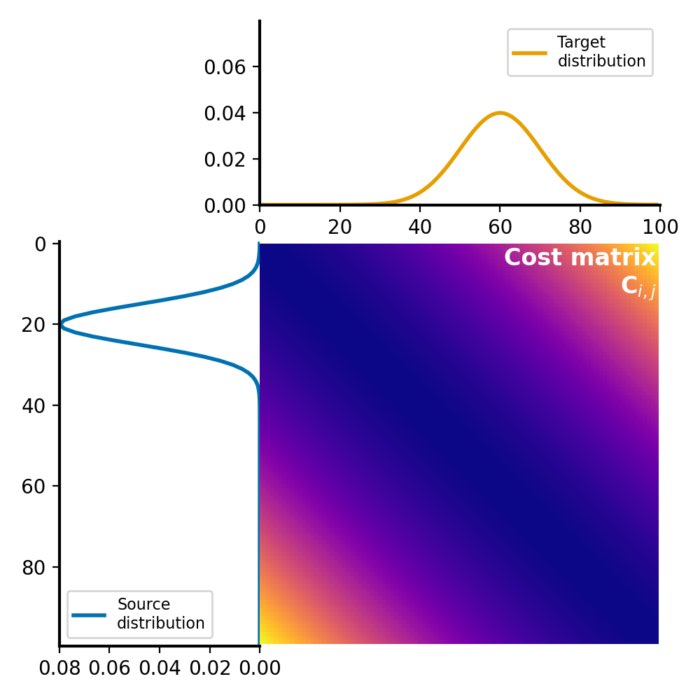
Wasserstein distance and optimal transport
The Wasserstein distance, also known as the Earth Mover’s Distance (EMD), provides a robust and i...
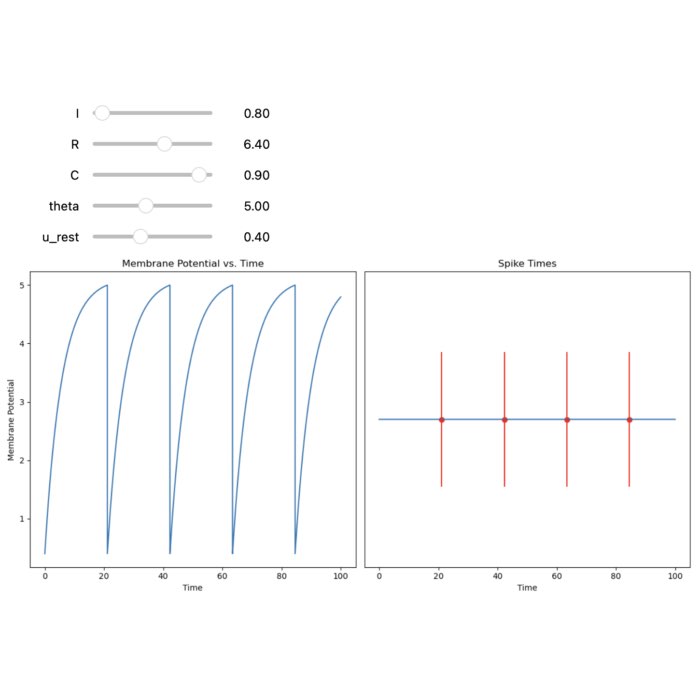
Integrate and Fire Model: A simple neuronal model
In this post we explore the Integrate-and-Fire model, a simplified representation of a neuron. We...
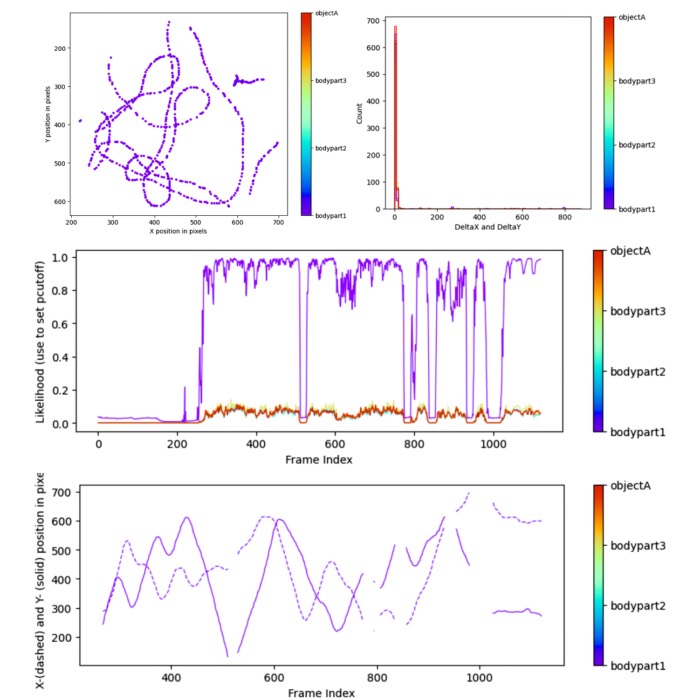
Assessing animal behavior with machine learning: New DeepLabCut tutorial
I have added a hands-on tutorial to the Assessing Animal Behavior lecture. The tutorial covers th...
Assessing animal behavior with machine learning
High-throughput and multi-modal behavior experiments, coupled with machine learning analysis, unl...
The Weierstrass function and the beauty of fractals
Fractals are captivating mathematical objects that exhibit intricate patterns and self-similarity...
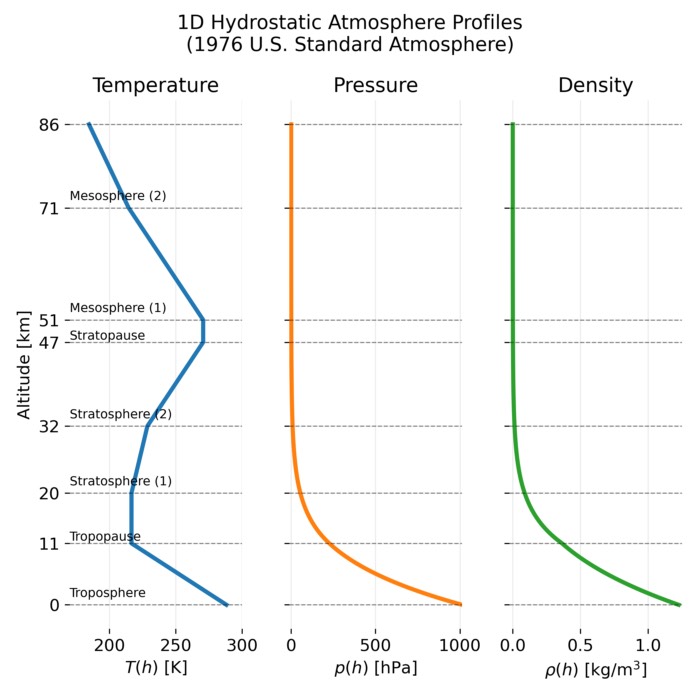
Atmosphere and ocean as hydrostatic fluids
Although atmospheric physics is today a well established and highly specialized research field, m...
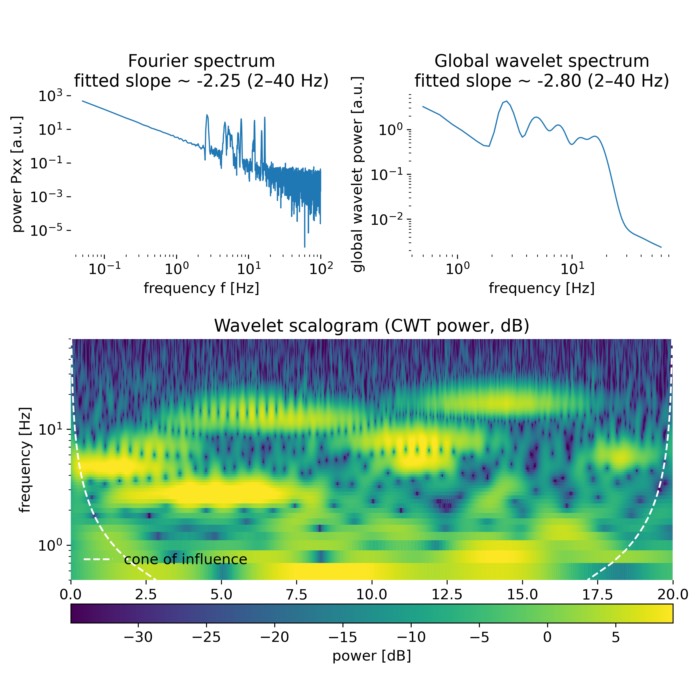
Wavelet analysis in turbulence (and beyond)
Wavelet analysis provides a joint time scale representation of signals, making it particularly su...
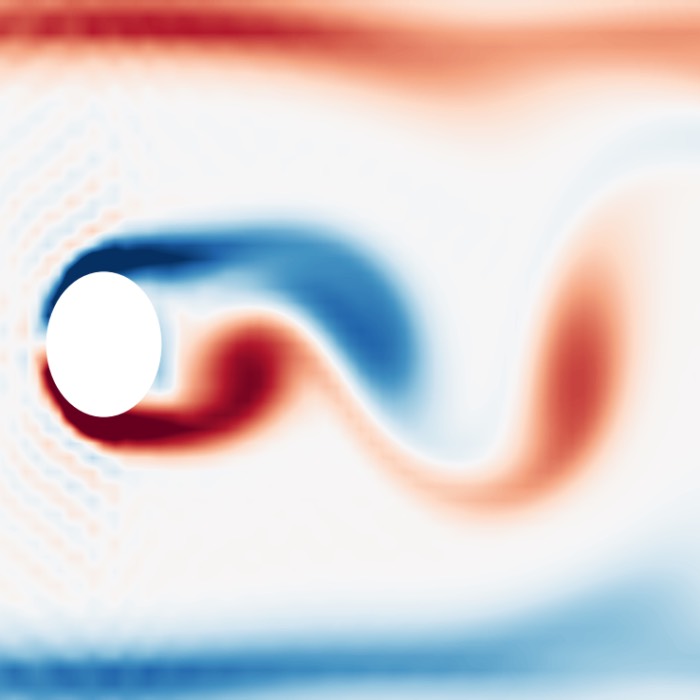
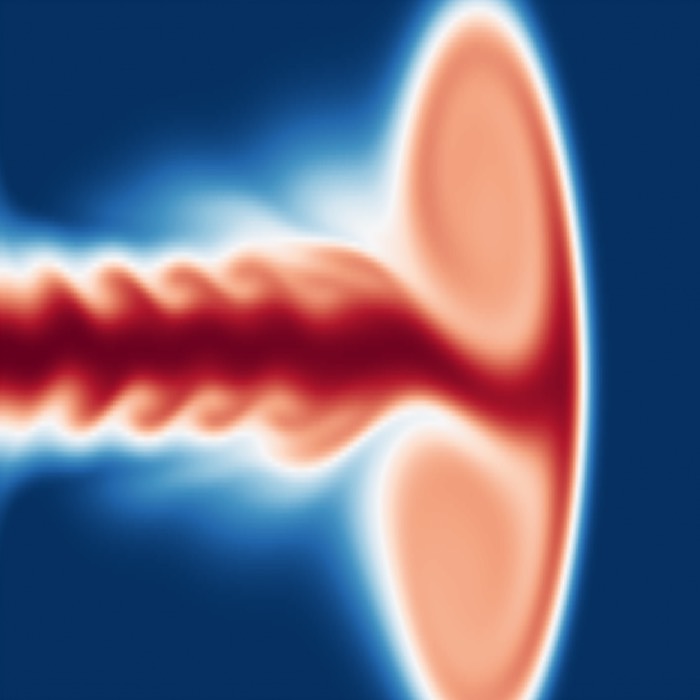
The von Kármán vortex street
One of the most iconic and visually striking examples of unsteady fluid flow is the von Kármán vo...
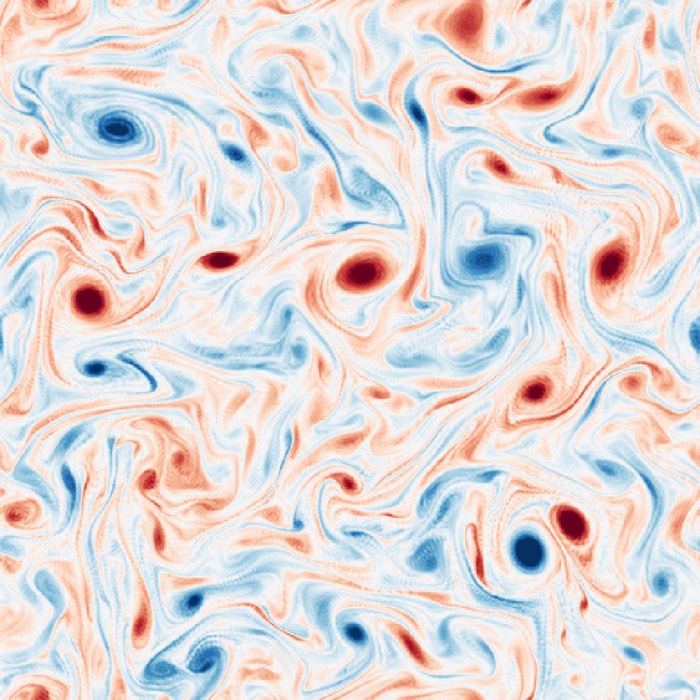
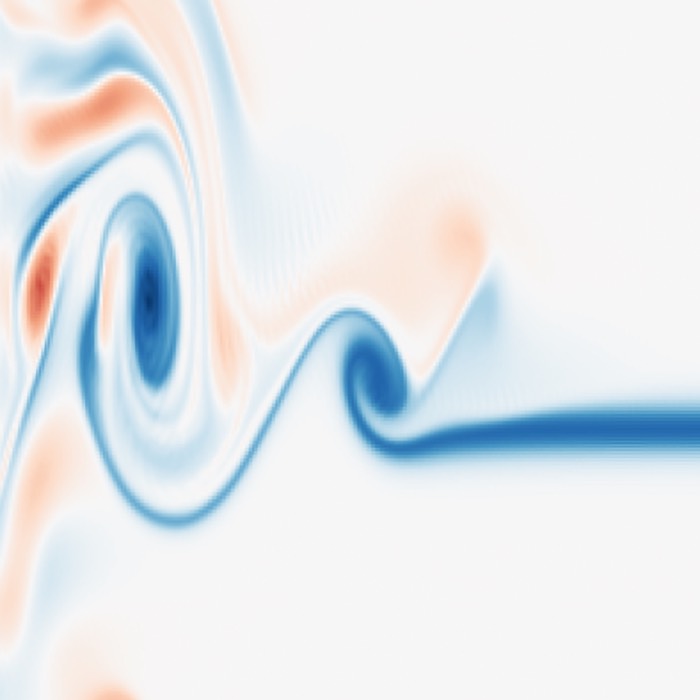
Forced 2D turbulence and Richardson cascade in a pseudospectral vorticity solver
In this post, we implement a forced two dimensional incompressible turbulence simulation in vorti...
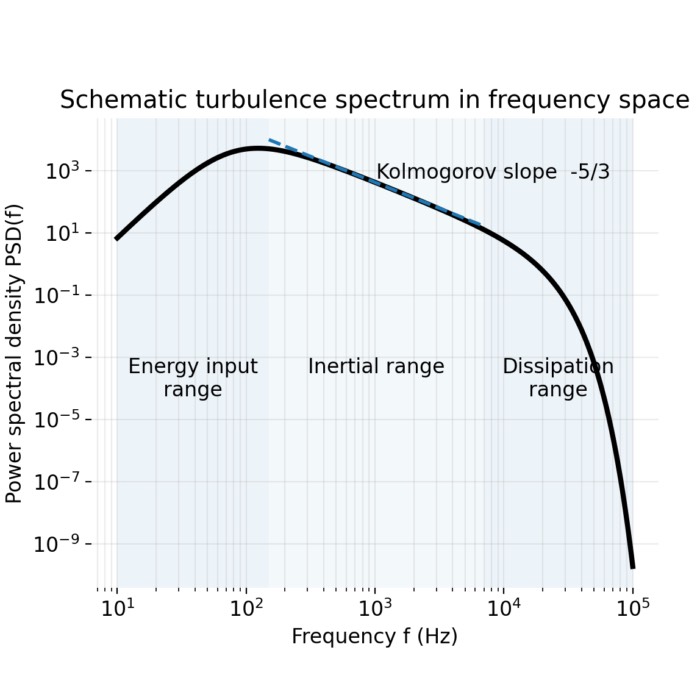
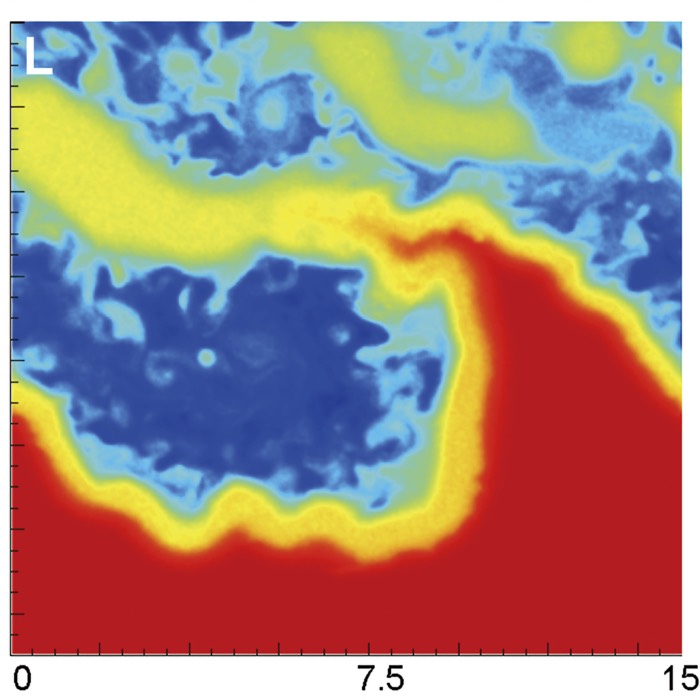
Turbulence, Richardson cascade, and spectral scaling in incompressible flows
Turbulence is a generic dynamical regime of fluids, independent of whether the medium is liquid, ...
Hydrodynamics: A brief overview of fluid dynamics and its fundamental equations
Hydrodynamics, the study of fluid motion, is a cornerstone of classical physics with applications...
A spatially developing 2D Kelvin Helmholtz jet with a finite volume projection method
In this post, we explore the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in a spatially developing 2D jet using ...
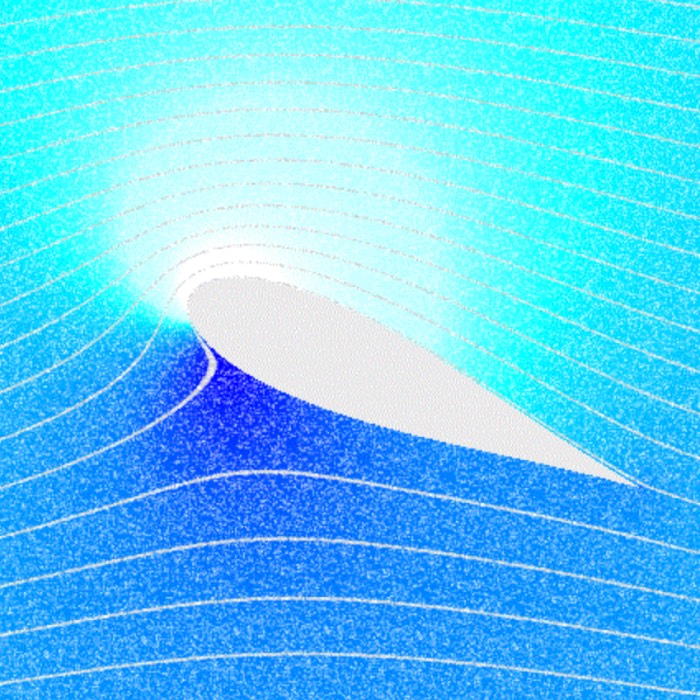
Kelvin–Helmholtz instability in 2D incompressible shear flows
The Kelvin–Helmholtz instability is a fundamental fluid dynamical phenomenon that occurs at the i...
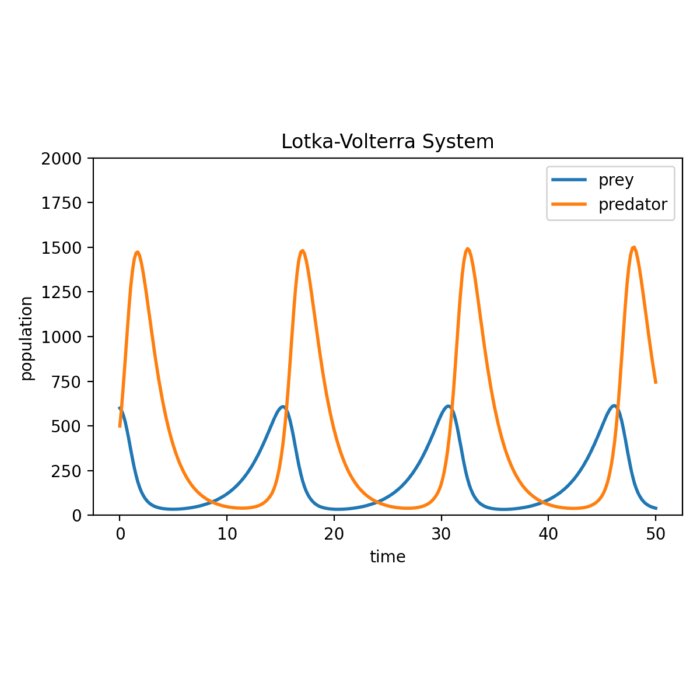
The Lotka-Volterra equations: Modeling predator-prey dynamics
The Lotka-Volterra system, also known as the predator-prey equations, is a mathematical model tha...
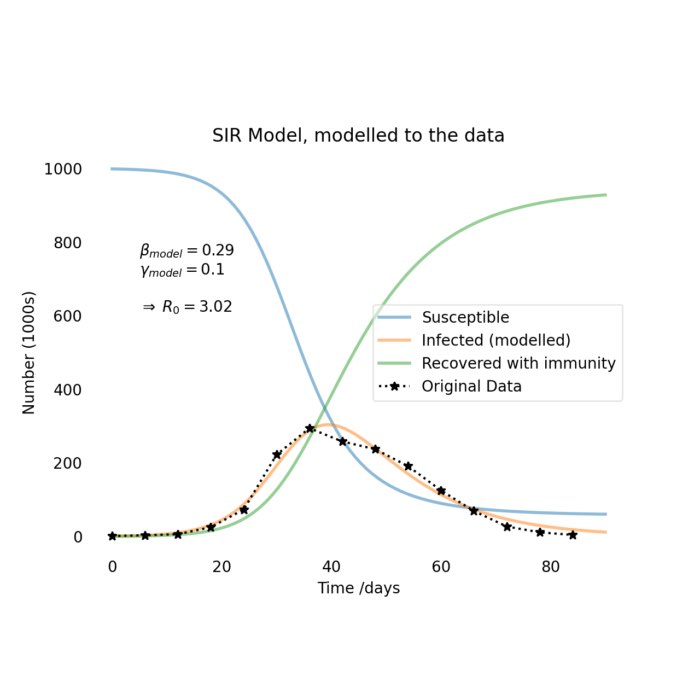
The SIR model: A mathematical approach to epidemic dynamics
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, epidemiological models have garnered significant attention ...
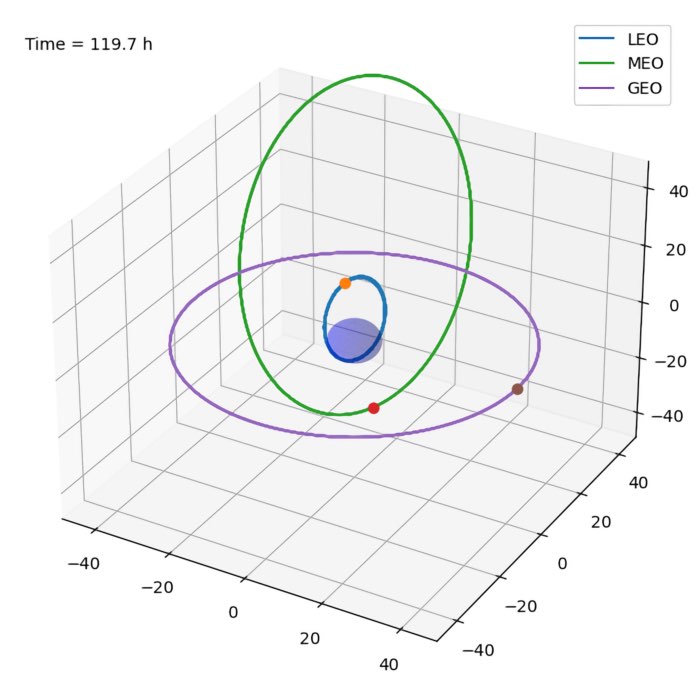
The two-body problem
The two-body system is a classical problem in physics. It describes the motion of two massive obj...
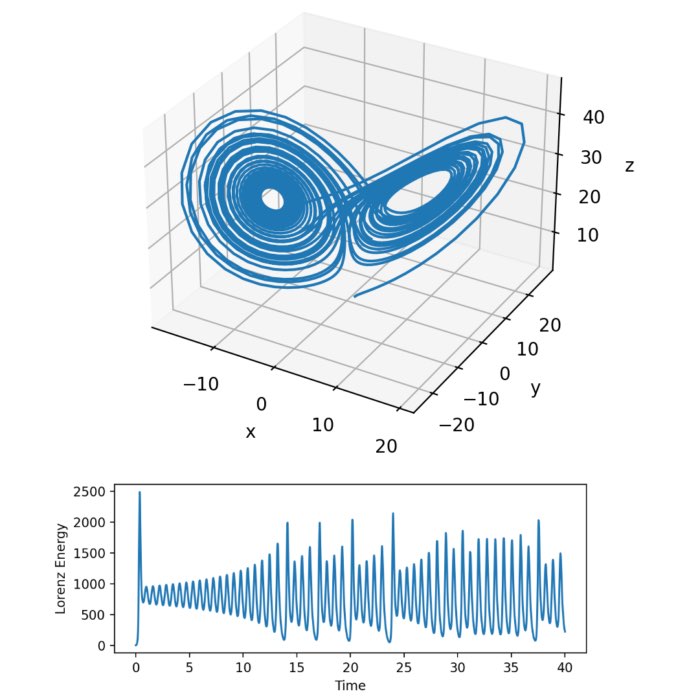
Solving the Lorenz system using Runge-Kutta methods
In my previous post, I introduced the Runge-Kutta methods for numerically solving ordinary differ...
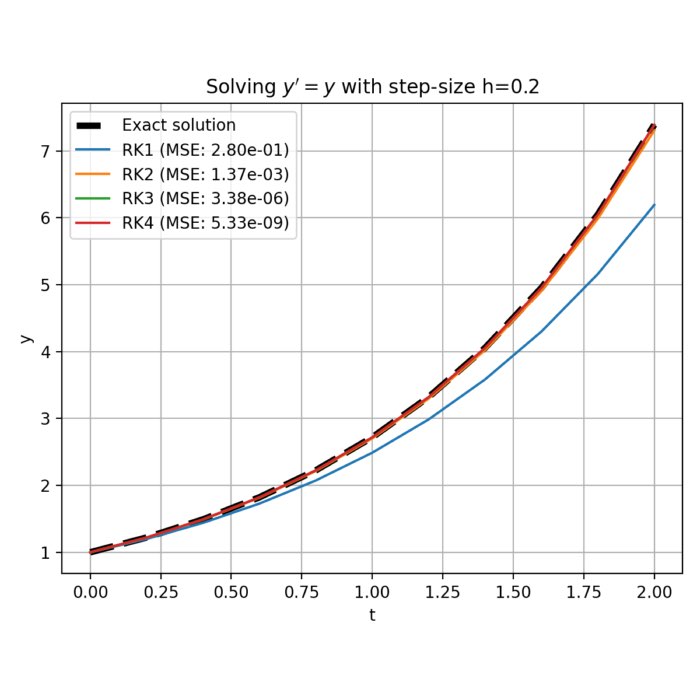
Runge-Kutta methods for solving ODEs
In physics and computational mathematics, numerical methods for solving ordinary differential equ...
A spectral (FFT) Poisson solver for 1D electrostatic PIC
In our previous post on Particle-in-Cell methods, we implemented a minimal 1D electrostatic PIC c...
Particle-in-Cell methods in kinetic plasma simulations
The Particle-in-Cell (PIC) method is a powerful numerical technique for simulating kinetic plasma...
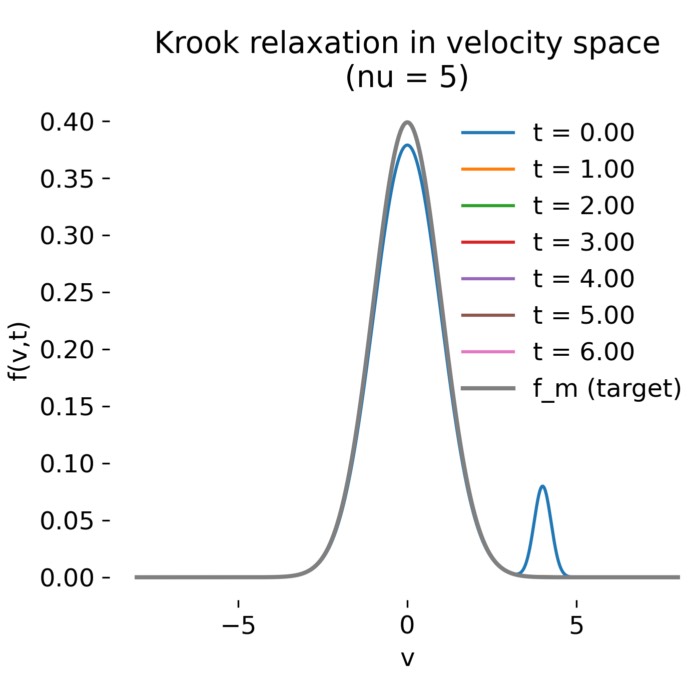
Krook collision operator as velocity-space relaxation
The Krook collision operator provides a minimal model for velocity-space relaxation in kinetic pl...
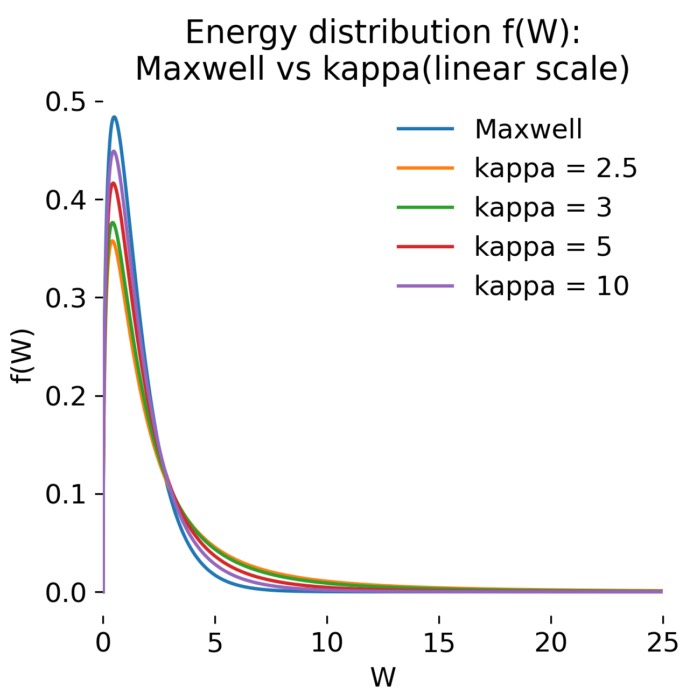
Kappa versus Maxwell distributions: Suprathermal tails in collisionless plasmas
In many space plasmas, particle velocity distributions deviate from the Maxwellian form due to we...
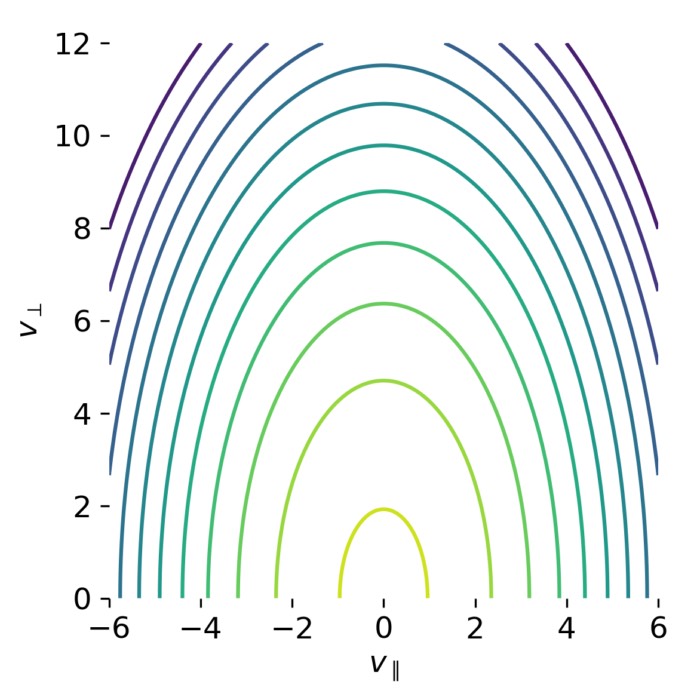
Bi-Maxwellian distributions and anisotropic pressure
In many space and laboratory plasmas, velocity distributions are anisotropic with respect to the ...
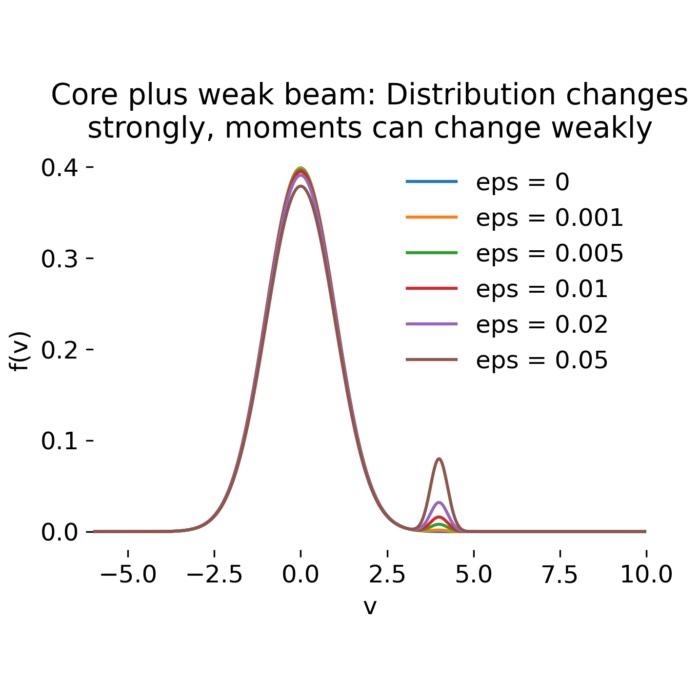
What velocity moments miss: Core plus beam distributions
In this post, we explore how different initial velocity distributions lead to qualitatively disti...
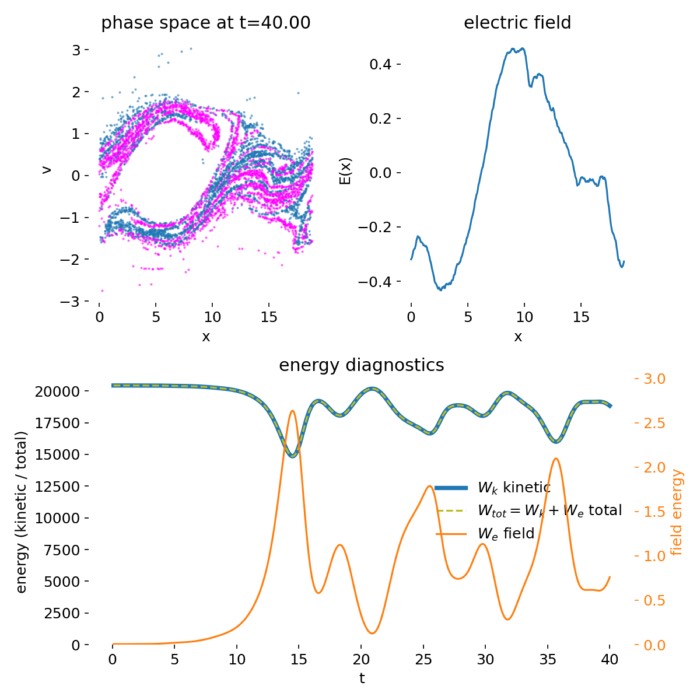
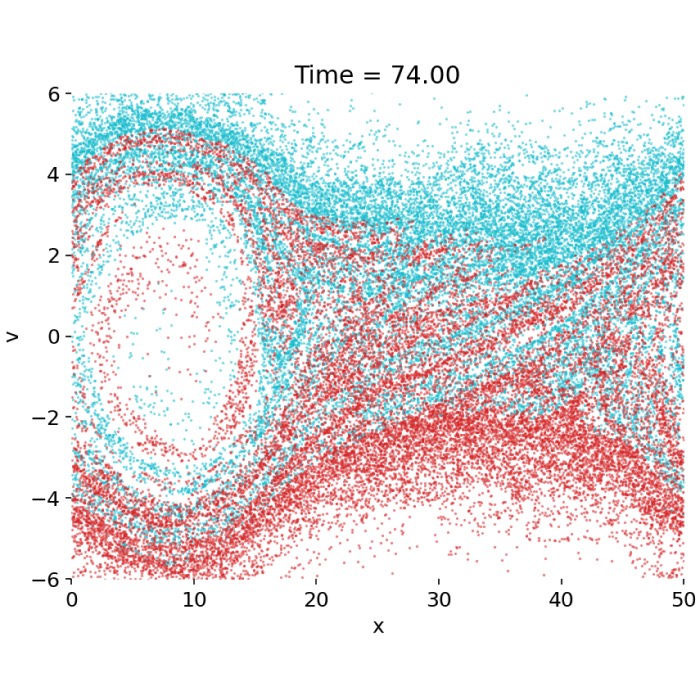
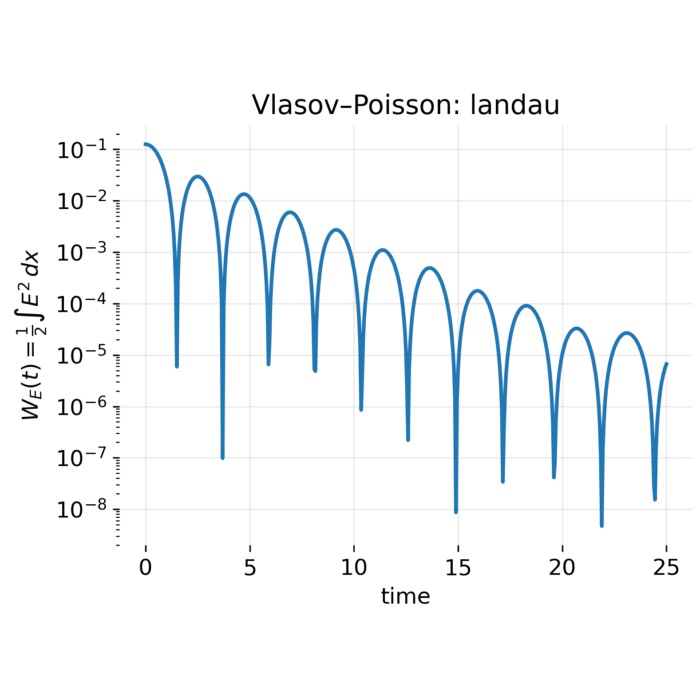
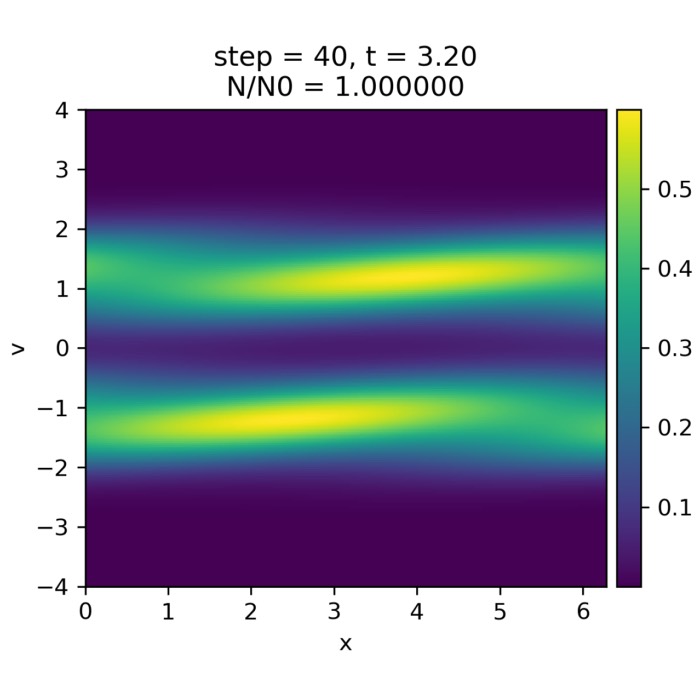
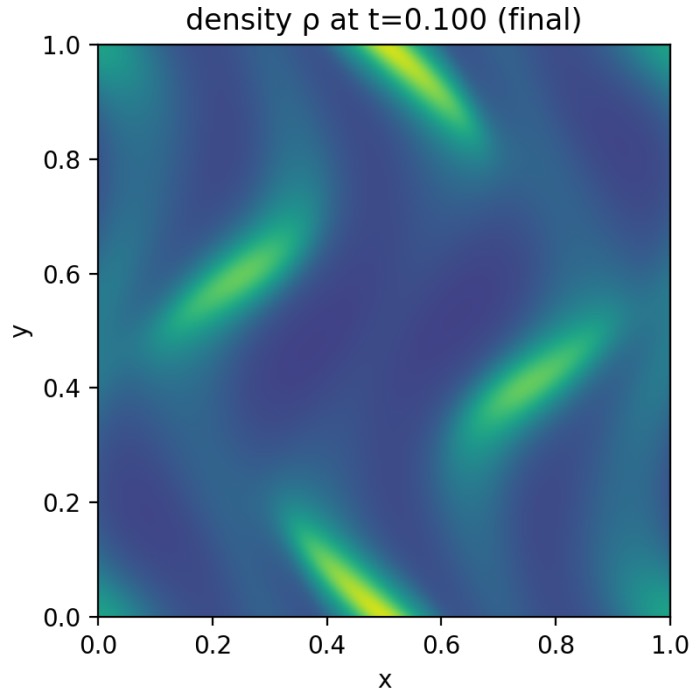
Vlasov–Poisson dynamics: Landau damping and the two-stream instability
The Vlasov–Poisson system provides a minimal kinetic framework to illustrate fundamental plasma p...
Kinetic plasma theory: From distribution functions to the Vlasov equation
Kinetic plasma theory describes a plasma as an ensemble of particles represented by a distributio...
Plasma instabilities as dynamical departures from equilibrium
Plasma instabilities mark the transition from passive wave propagation to active energy conversio...
The Alfvén wave as a fundamental mode of magnetized plasmas
Among all plasma waves, the Alfvén wave occupies a special conceptual position. It is the simples...
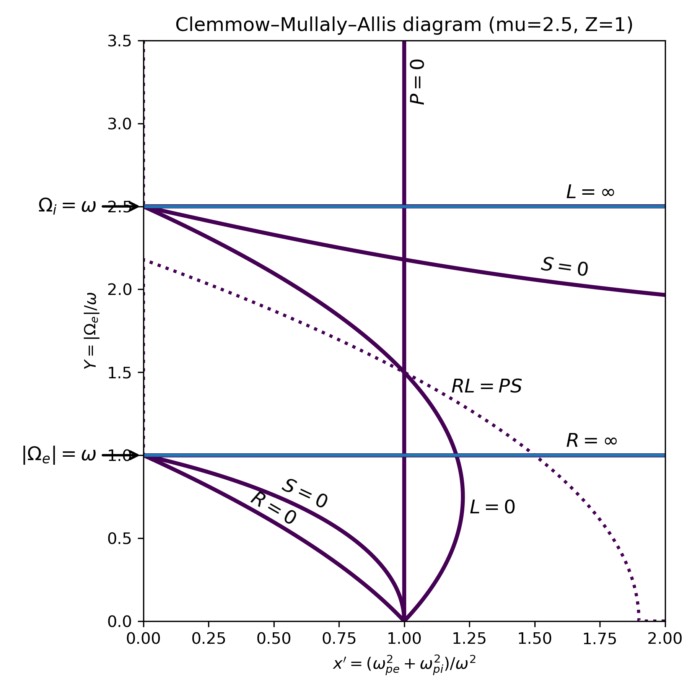
Plasma waves in space plasmas
Space plasmas support a rich spectrum of collective wave phenomena that have no direct analogue i...
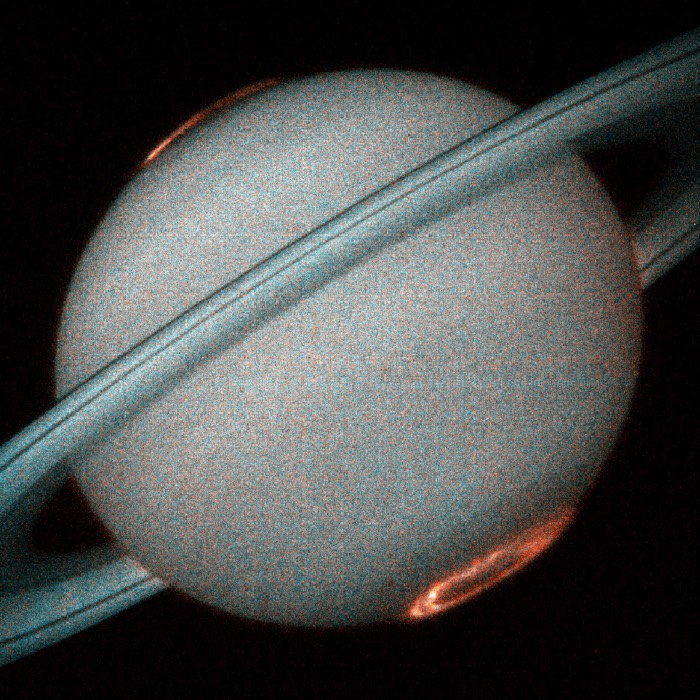
Planetary aurorae
Planetary aurorae are luminous phenomena that occur in the upper atmospheres of magnetized planet...
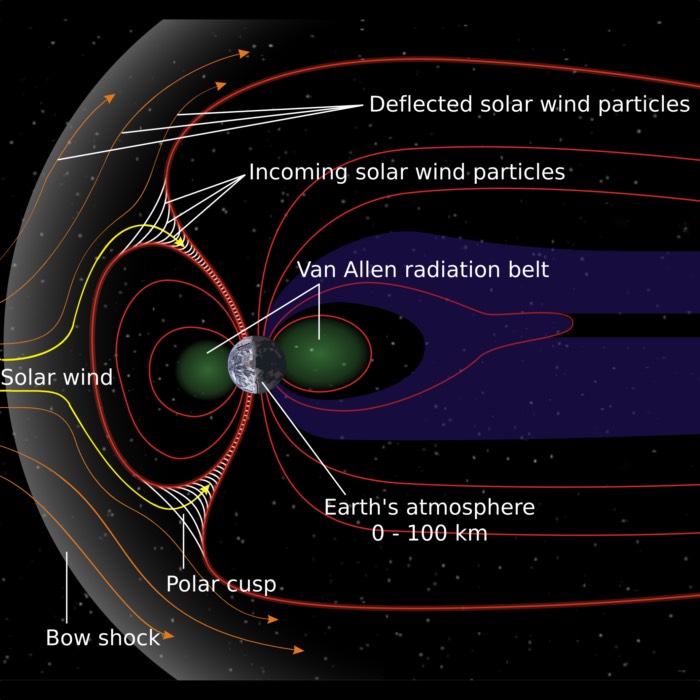
Space Physics: A definitional perspective
Space physics is more than plasma physics. It is an extension of geophysics into space, applying ...
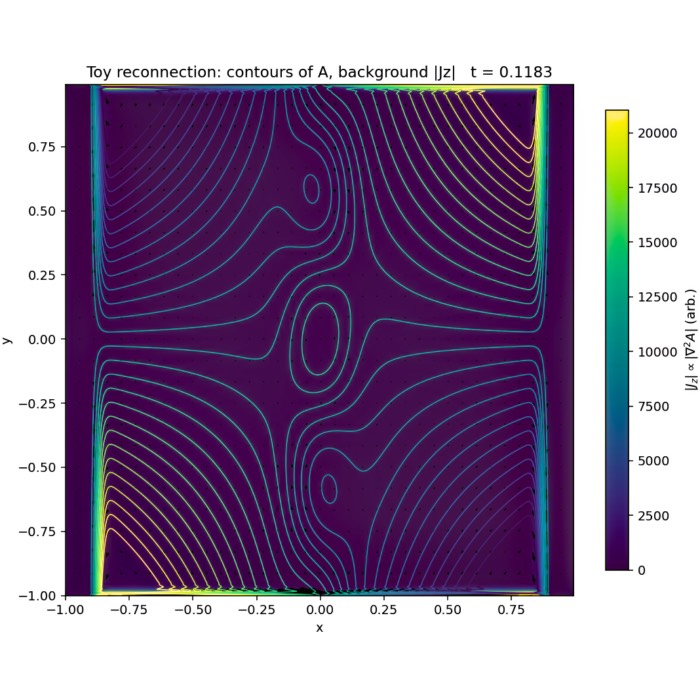
Magnetic reconnection via X-point collapse
In this post, we explore a complementary toy model of magnetic reconnection based on the collapse...
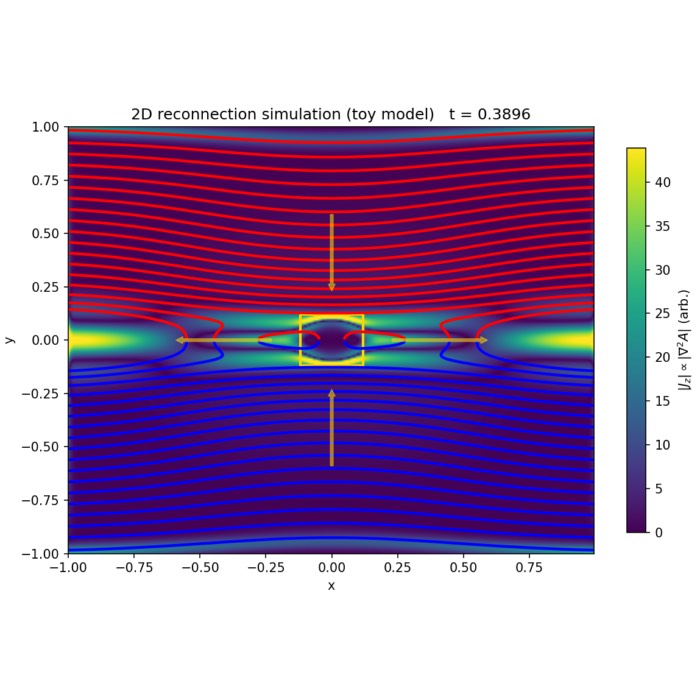
Magnetic reconnection: Theory and a simple numerical model
Magnetic reconnection is a fundamental plasma process that changes magnetic field topology and co...
The solar wind and the Parker model
The solar wind is a continuous, supersonic outflow of ionized plasma from the solar corona into i...
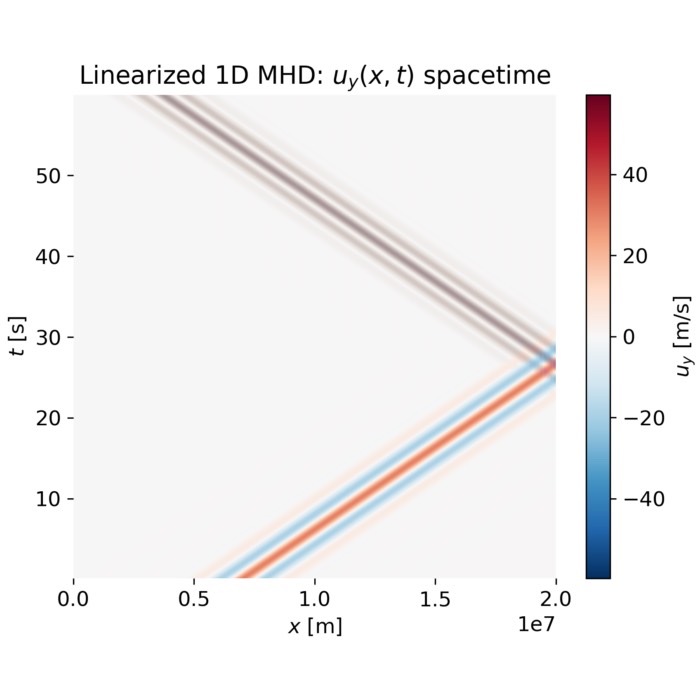
Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD): A theoretical overview with a numerical toy example
Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) describes the coupled dynamics of a conducting fluid and electromagnet...
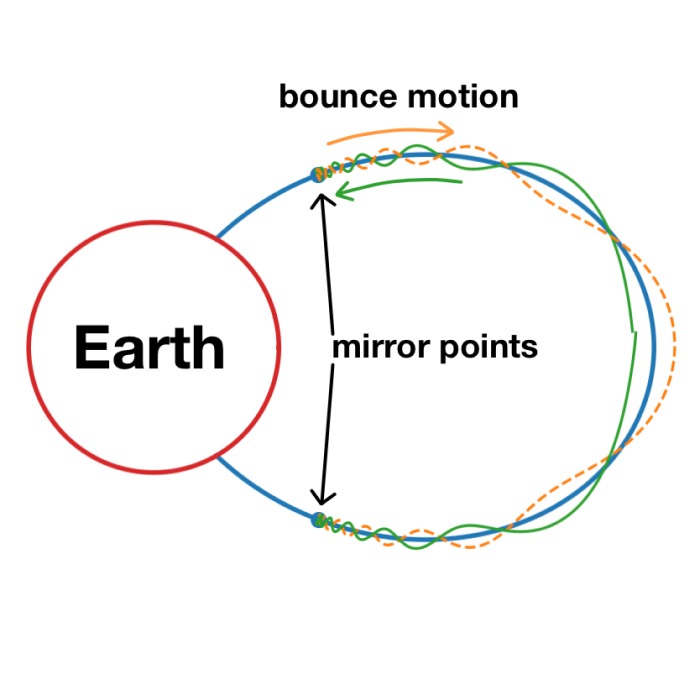
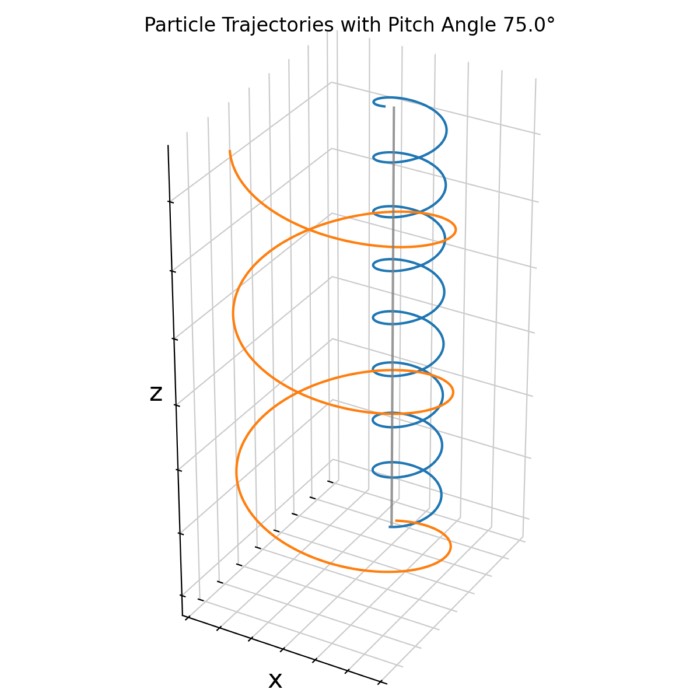
Adiabatic invariants and magnetic mirrors
Adiabatic invariants provide the central simplification behind most practical descriptions of cha...
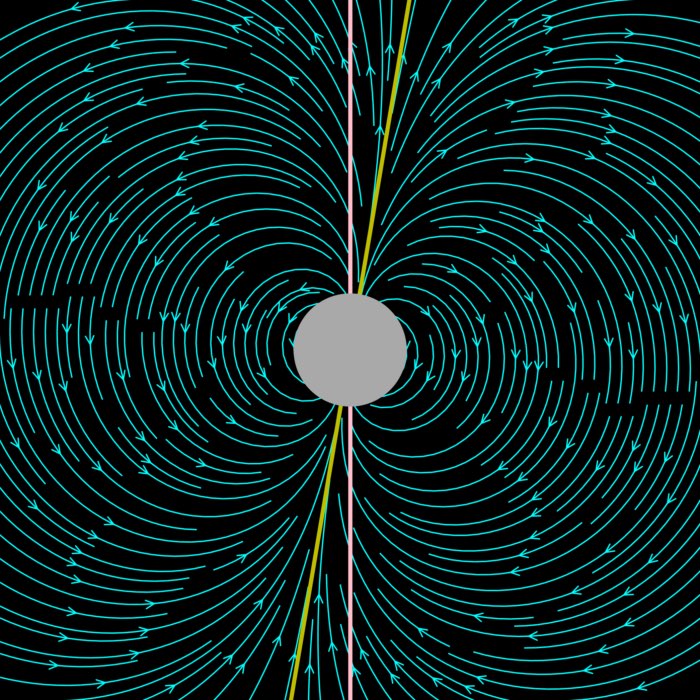
Earth’s dipolar magnetic field
In physics and computational mathematics, numerical methods for solving ordinary differential equ...
Single-particle description of plasmas: Equation of motion, gyration, and ExB drift
In plasma physics, the motion of a single charged particle in prescribed electromagnetic fields p...
Characteristics of a plasma: Collective behavior, shielding, and intrinsic time scales
Both in space and astrophysics as well as in laboratory settings, plasma is the most common state...